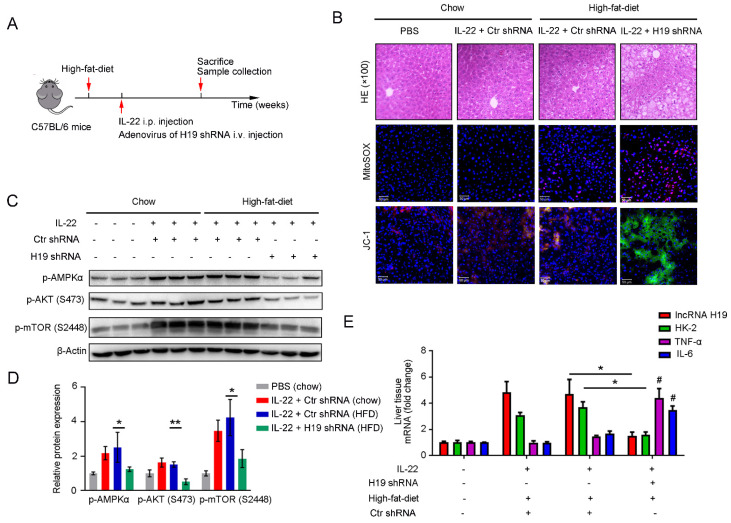
Figure 7.
IL-22 attenuates hepatic oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction and damage through the induction of lncRNA H19. (A) Schematic diagram of the animal experimental protocols to assess the effects of IL-22 (2.5 mg/kg) and H19 shRNA (1x1010 virus particles per mouse) in high-fat-diet fed mice (n = 8). PBS and Control shRNA (Ctr shRNA) treated mice as a vehicle control group (n = 5). (B) Representative HE, MitoSOX, and JC-1 staining images of the liver sections were presented. (C) Western blotting suggested that IL-22 induced AMPK/AKT/mTOR activation in liver via the induction of lncRNA H19. (D) Densitometric values were quantified and normalized to control group (n = 3; mean ± SD; *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01). The values of control group were set to 1. (E) The mRNA expression levels of the indicated genes in the liver (n = 3). *P ≤ 0.05 compared with H19 shRNA-treated mice. #P ≤ 0.05 compared with IL-22-treated and high-fat-diet fed mice. All data are means ± SD of at least three independent experiments.