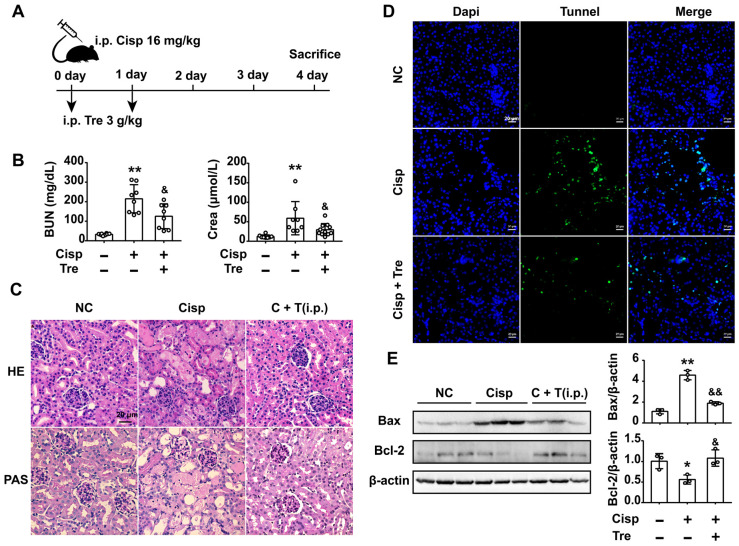
Figure 7.
Intraperitoneal (i.p.) injection of trehalose protects the kidney against cisplatin-induced AKI. (A) Mice were intraperitoneally injected with a single dose of cisplatin (16 mg/kg BW) to induce AKI and then intraperitoneally administered trehalose (3 g/kg BW) at the same time for 2 days. (B) Serum BUN and Crea levels were quantified in each group (n = 8 - 11 mice). (C) Representative images of HE- and PAS-stained kidney sections. (D) Representative micrographs showing TUNEL staining. (E) Representative images of western blotting and the quantitative analyses of Bax and Bcl-2 (n = 3 mice). Data analyzed by one-way ANOVA with Tukey's test. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01 vs. Con; & P < 0.05, && P < 0.01 vs. Cisp. (NC, normal control; Cisp, cisplatin; Tre, trehalose; C + T, cisplatin + trehalose; i.p., intraperitoneal; BUN, blood urea nitrogen; Crea, serum creatinine; HE, hematoxylin/eosin; PAS, periodic acid-Schiff; TUNEL, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase-mediated dUTP nick-end labeling staining).