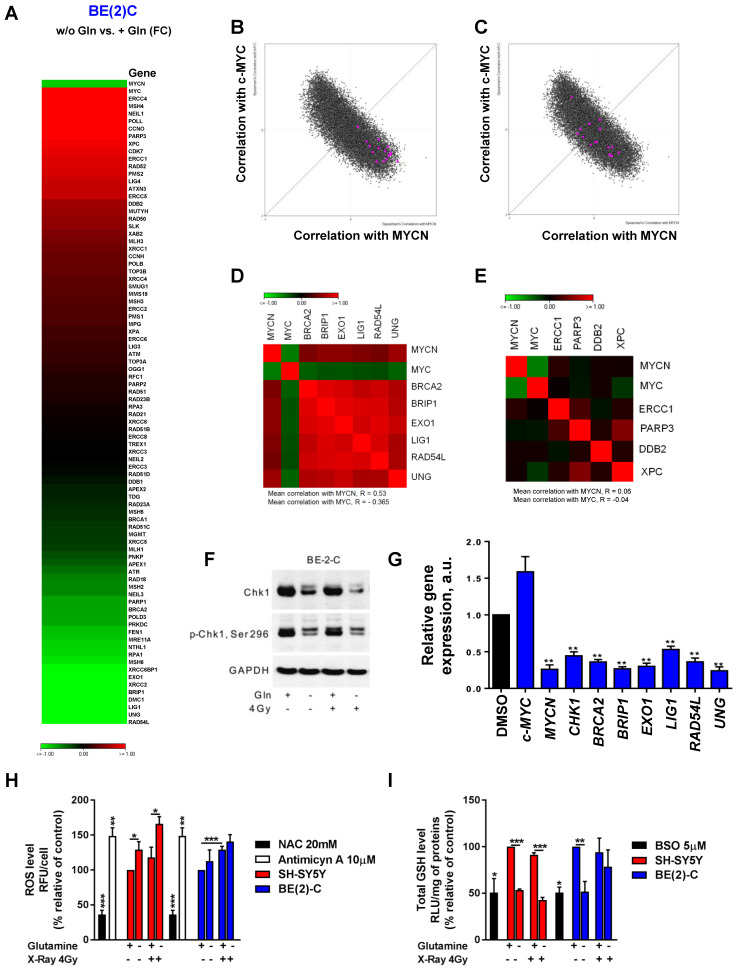
Figure 5.
Glutamine deprivation modifies DNA repair gene pathway and redox balance in neuroblastoma cells. (A) Expression levels of 84 DNA repair genes analyzed using DNA RT² Profiler PCR Array Human DNA Repair in BE(2)-C cells upon 24 h of glutamine deprivation. Data are from two pooled experiments. (B, C) Correlation of mRNA expression for (B) 17 genes downregulated upon glutamine deprivation and (C) 16 genes upregulated upon glutamine starvation with c-MYC and MYCN genes in the neuroblastoma TARGET patient cohort. (D, E) Correlation map for (D) 6 clinically relevant genes, which were downregulated upon glutamine deprivation and (E) 4 clinically relevant genes, which were upregulated upon glutamine deprivation, with c-MYC and MYCN. (F) Representative western blot of total Chk1 and p-Chk1 levels in BE(2)-C cells upon glutamine deprivation and irradiation (4 Gy). GAPDH was used as a loading control. (G) Relative mRNA expression of CHK1, MYCN, c-MYC and 6 DNA repair genes upon glutamine deprivation in BE(2)-C cells. (H) Analysis of ROS levels in SH-SY5Y (red) and BE(2)-C (blue) cells upon 48 h glutamine deprivation and 4 Gy X-rays. NAC and antimycin A used as negative and positive controls. Data are reported as averages relative to control (n = 3; ± S.E.M; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001). (I) Analysis of total GSH levels in SH-SY5Y (red) and BE(2)-C (blue) cells upon 48 h glutamine deprivation and 4 Gy X-rays. BSO used as positive control. Data are reported as averages relative to control (n = 3; ± S.E.M; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001).