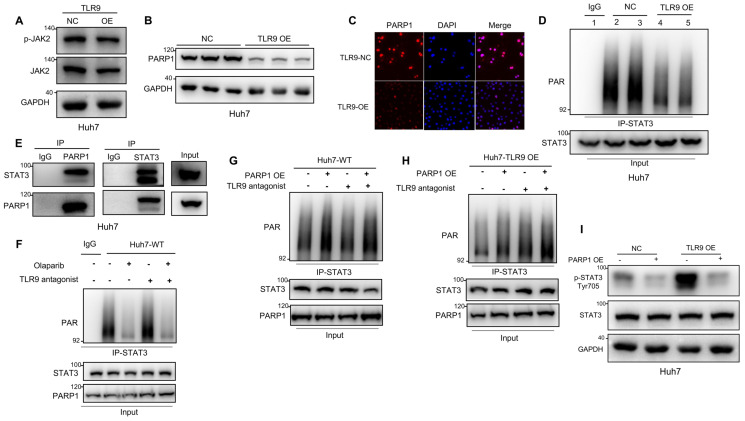
Figure 3.
TLR9 activation promoted STAT3 Tyr705 phosphorylation through PARP1-mediated STAT3 PARylation. (A) p-JAK level after exogenous TLR9 overexpression in Huh7 cells. p-JAK expression levels were analyzed by Western blotting. (B and C) PARP1 levels after TLR9 overexpression. PARP1 levels were analyzed by Western blotting or immunofluorescence. (D) PARylated STAT3 level after TLR9 overexpression in Huh7 cells. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using anti-IgG or anti-STAT3 antibodies and immunoblotted using an anti-PAR antibody. (E) Interaction between endogenous STAT3 and PARP1. Huh7 cell lysates were immunoprecipitated with anti-PARP1 or anti-STAT3 antibodies, followed by immunoblotting with an anti-STAT3 or anti-PARP1 antibody. (F) PARylated STAT3 level in wild-type Huh7 cells in the presence of the PARP inhibitor olaparib or TLR9 antagonist chloroquine diphosphate. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using anti-IgG or anti-STAT3 antibodies and immunoblotted using an anti-PAR antibody. (G and H) PARylated STAT3 levels in wild-type (G) or TLR9-overexpressing (H) Huh7 cells in the presence of exogenous PARP1 overexpression or the TLR9 antagonist chloroquine diphosphate. Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated using anti-IgG or anti-STAT3 antibodies and immunoblotted using an anti-PAR antibody. (I) p-STAT3 (Tyr705) levels after exogenous PARP1 overexpression in TLR9-overexpressing Huh7 cells. p-STAT3 (Tyr705) levels were analyzed after TLR9 overexpression alone or in the presence of PARP1 overexpression.