Figure 3. Proposed catalytic mechanism of hDGAT1.
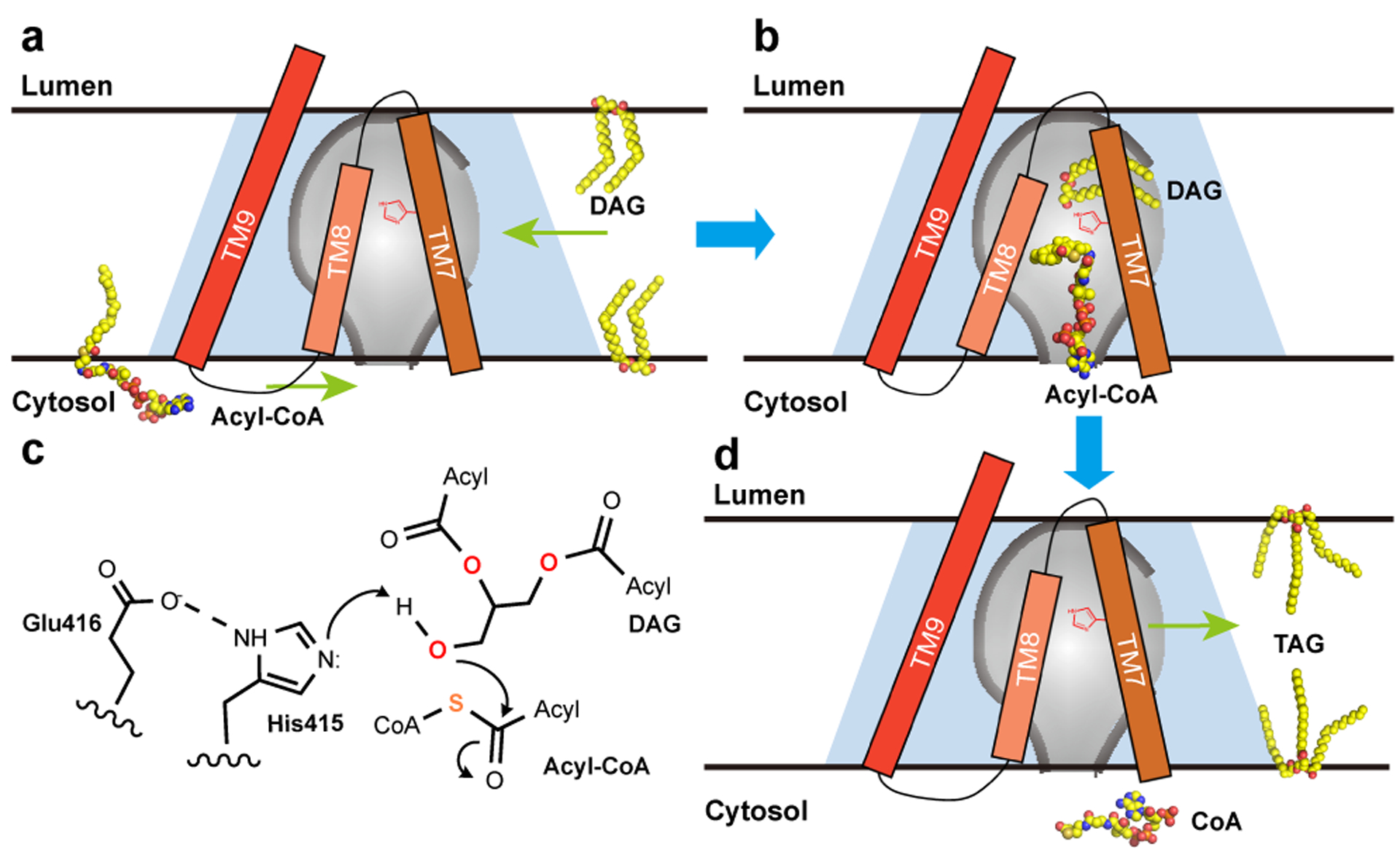
a. and b. An hDGAT1 monomer is shown as a trapezoid in light blue and the reaction chamber in the shape of an inverted flask colored in grey. TM7–9, acyl-CoA and DAG are shown schematically. The catalytic His415 is marked in red on TM7. The CoA moiety of an acyl-CoA binds to hDGAT1 at the cytosolic entrance of the tunnel and the hydrophobic acyl chain slides into the reaction chamber through a slit between TM7 and TM8. The glycerol backbone of DAG enters the chamber from the large side entrance with the two acyl-chains partially hosted in the hydrophobic core of the membrane. c. Proposed catalytic mechanism. E416 and H415 activate the 3-hydroxyl on DAG for a nucleophilic attack on the thioester of the Acyl-CoA. d. After the reaction, the product TG could diffuse into either leaflet of the membrane.
