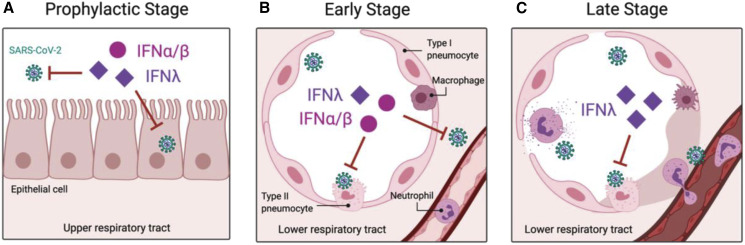
Figure 3.
Therapeutic Aims with Type I and Type III IFNs during the Progression of COVID-19
(Α) Prophylactic intranasal administration or inhalation of recombinant IFNs, particularly type III IFNs (IFN-λ), can act to restrict viral replication in the upper airway, reducing viral spread to the lungs and transmission.
(Β) When initial control fails and virus reaches the lung, the host may benefit from additional IFNs, including the more potent type I IFNs (IFN-α, IFN-β). Given that our natural IFN response may be lacking at this early stage, exogenous IFNs might help control infection and prevent viral dissemination.
(C) In the late stage of the disease, IFNs must be used with caution to not exacerbate inflammation and tissue damage. IFN-λ could continue to activate localized antiviral protection without triggering a systemic response.