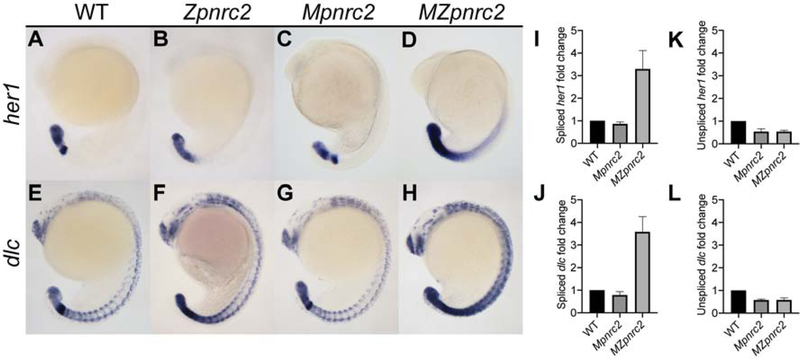
Figure 1. Maternal and zygotic pnrc2 promotes proper her1 and dlc expression.
Wild-type (WT), zygotic pnrc2oz22 (Zpnrc2), maternal pnrc2oz22 (Mpnrc2), and maternal-zygotic pnrc2oz22 (MZpnrc2) mutant embryos were raised to mid-segmentation stage (16–18 hpf) and probed for her1 (A–D) and dlc expression (E–F) by in situ hybridization (n ≥ 7 each). WT, Mpnrc2 mutant, and MZpnrc2 mutant embryos (n = 10 per biological replicate) were analyzed by qPCR using primers to amplify across exon-exon boundaries to detect spliced her1 (I) and dlc (J) transcripts or primers to amplify across intron-exon boundaries to detect her1 (K) and dlc (L) unspliced transcripts. MZpnrc2 mutant embryos have ~4-fold higher levels of spliced her1 and dlc mRNA than wild-type or Mpnrc2 mutant embryos, which have comparable levels (I and J). Both MZpnrc2 and Mpnrc2 mutant embryos have ~2-fold less unspliced her1 and dlc transcripts compared to WT embryos (K and L). hpf = hours post-fertilization.