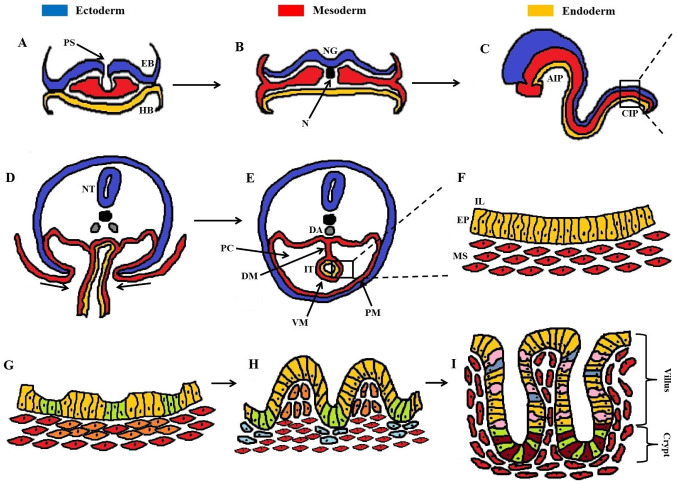
Figure 1.
Developmental stages of the intestinal epithelium. (A) Gastrulation with migration of cells from the primitive streak, performing either EMT and/or MET. (B) Formation of the three germinal layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm). (C) The primitive gut tube is formed through invaginations in the AIP and CIP, consisting of the endoderm (internally) underlying the mesoderm (externally). (D) Cross-section of the rectangular area in (C), showing the ventral invagi-nations of mesoderm. (E) Formation of the peritoneal cavity around the closed IT, with PM and VM. (F) Magnification of the rectangular area in (E), showing the pseudostratified structure of the intestinal epithelium (EP, yellow cells) and underlying mesenchyme (MS, red cells). (G) Formation of mesenchymal clusters (orange cells) as a response to epithelial signaling, marking the onset of villus morphogenesis. (H) Progressive epithelial remodeling via mesenchymal signaling polarizes the columnar epithelial cells into shaping stereotypical villi (yellow cells) and proliferative intervilli (green cells). Mesenchymal clusters at the top of villi prevent further epithelial proliferation through post-mitotic signaling, whereas clusters below the intervilli (blue cells) regulate the division of intestinal stem cells. (I) Maturation of intestinal epithelium with definite formation of villi and crypts housing mostly enterocytes (yellow cells), goblet cells (pink cells), and enteroendocrine cells (blue cells). At the base of the crypt the cellular populations are mainly dominated by secretory Paneth cells (dark red cells) and proliferative intestinal stem cells (green cells). A dense network of myofibroblasts (red cells) underlies the intestinal epithelium. AIP, anterior intestinal portal; CIP, caudal intestinal portal; DA, dorsal aorta; DM, dorsal mesentery; EB, epiblast; EMT, epithelial-mesenchymal transition; EP, epithelium; HB, hypoblast; IL, intestinal lumen; IT, intestinal tube; MET, mesenchymal-epithelial transition; MS, mesenchyme; N, notochord; NG, neural groove; NT, neural tube; PC, peritoneal cavity; PM, parietal mesoderm; PS, primitive streak; VM, visceral mesoderm.