FIGURE 5.
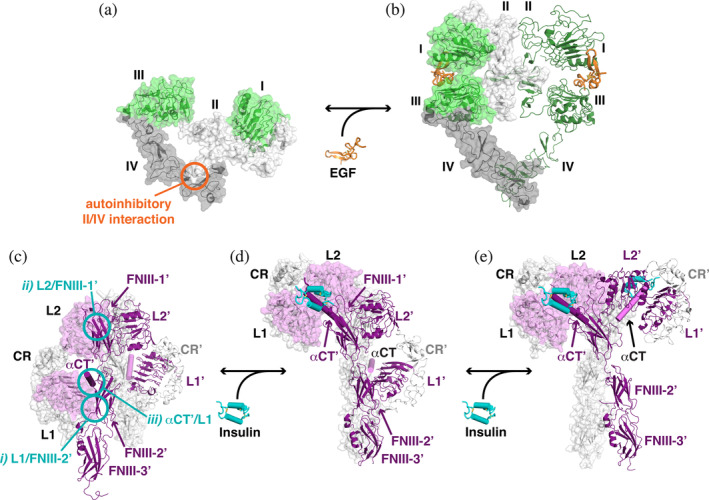
Coupling of L1‐CR‐L2 module closure to altered EGFR and IR dimerization. (a) An unliganded EGFR monomer (pdb id 1yy9) is shown as a cartoon with transparent surface. Domains I and III are green, domain II is light gray, and domain IV is darker gray. The autoinhibitory intramolecular interaction between domains II and IV is marked with an orange circle. (b) The EGF‐bound EGFR ECR dimer is shown with a transparent surface, adopting an extended conformation (pdb id 3njp). (c, d) To appreciate the changes that occur in IR upon ligand binding, structures of unliganded, singly liganded, and fully liganded dimers have been aligned using the coordinates of the FNIII‐1/FNIII‐1′ pair. (c) The unliganded symmetric IR dimer from X‐ray crystallographic studies (pdb id 4zxb) is shown. The left‐hand molecule has a transparent gray surface, with the exception of L1 and L2, for which the surface is colored light magenta. The αCT is also shown as a light magenta cylinder. The second molecule is shown with L1′, L2′, and the FNIII domains as darker purple cartoons, αCT′ as a dark purple cylinder, and CR′ as light gray cartoon. Intermolecular autoinhibitory interactions between (i) L1 and FNIII‐2′, (ii) L2 and FNIII‐1′, and (iii) L1 and αCT′ are highlighted with cyan circles (the symmetry equivalents are not shown). (d) The asymmetric singly liganded IR dimer (pdb id 6hn5 and 6hn4), with the same representation and coloring as in (c). The single bound insulin molecule is shown in cyan with cylindrical helices (and interacts with αCT′, shown in dark purple and labeled). The location of αCT (light magenta), which was not included in pdb id 6hn4 as it was not well ordered, is modeled based on its location relative to L1′ in the unliganded structure. (e) The symmetric IR dimer (pdb id 6pxv) is shown with two bound insulin molecules. For clarity, the additional two insulin molecules in this structure that bind near FNIII‐1 and FNIII‐1′ (see text) are not shown. CR, cysteine‐rich; ECR, extracellular region; EGF, epidermal growth factor; EGFR, epidermal growth factor receptor; FNIII, fibronectin type III; IR, insulin receptor
