FIGURE 3.
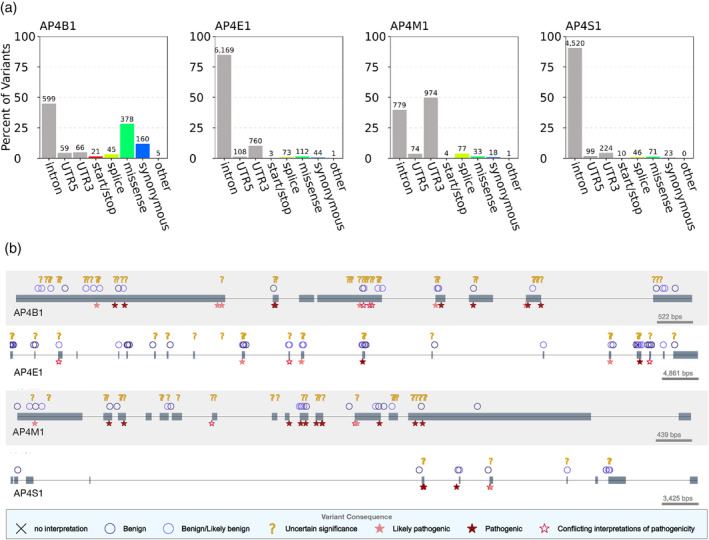
AP‐4 subunits harbor benign, disease‐associated, and uncharacterized human genetic variation. (a) Distribution of genic contexts of AP‐4 subunit genetic variants. We queried all variants occurring within the four AP‐4 genes in databases of human genetic variation across more than 140,000 individuals (1,000 Genomes and gnomAD). Variants were annotated based on their genic context (intron, UTR, coding) and functional impact on protein product (start/stop: gain or loss of transcription start or stop; splice: variant influencing splicing; missense; synonymous; or other: coding variants with missing label). The majority of variants are noncoding but many variants that influence coding sequence (missense, synonymous, splice) are present in each subunit. (b) Clinical consequences of AP‐4 variants. We plotted variants extracted from ClinVar along the gene body of each AP‐4 subunit (one row per AP‐4 subunit). Gray boxes represent exons occurring in known transcripts. Variants are displayed based on their predicted clinical consequence as reported in ClinVar. While several variants are known to be benign or pathogenic, more than 100 remain of uncertain significance. AP‐4, adapter protein complex 4
