FIGURE 5.
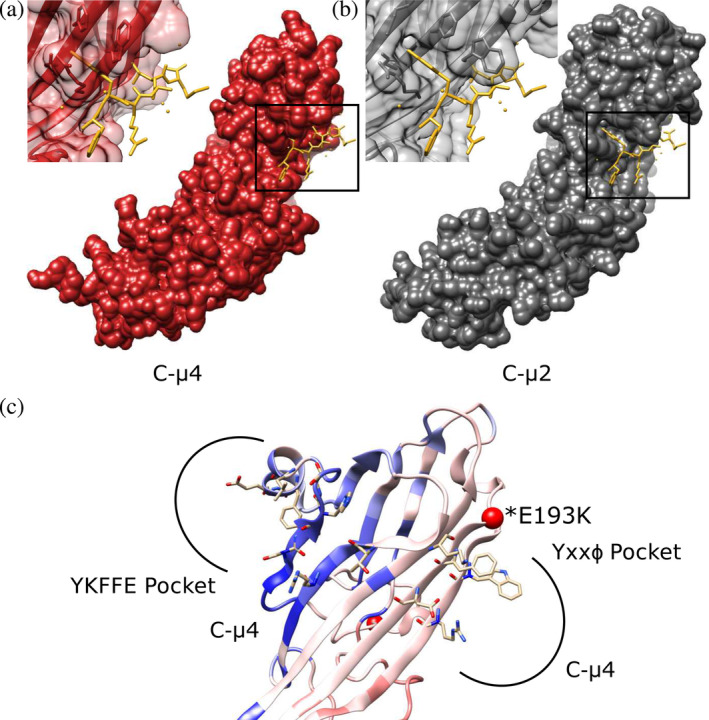
C‐μ4 cargo binding pockets. (a) The predicted Yxxφ binding pocket in C‐μ4 (PDB: 3L81) is shown with Yxxφ peptide from C‐μ2 superimposed (PDB: 1BW8). (b) The C‐μ2 Yxxφ cargo binding pocket with Yxxφ superimposed (PDB: 1BW8). C‐μ4 lacks the deep hydrophobic pocket known to accommodate the Tyr residue in canonical endocytic Yxxφ motifs. (c) Both YKFFE and Yxxφ binding pockets are shown mapped onto the PathProx C‐μ4 model. Residues important for motif binding in both pockets are shown as sticks. PathProx analysis indicates regions proximal to known pathogenic variation (mapped in red) and regions closer to benign variants (mapped in blue). Confirmed pathogenic mutation E193K shown as a red sphere. Current data suggest the Yxxφ binding pocket is more susceptible to pathogenicity, although the YKFFE site is believed to be important for sorting AP‐4 cargoes like ATG9. AP‐4, adapter protein complex 4
