FIGURE 6.
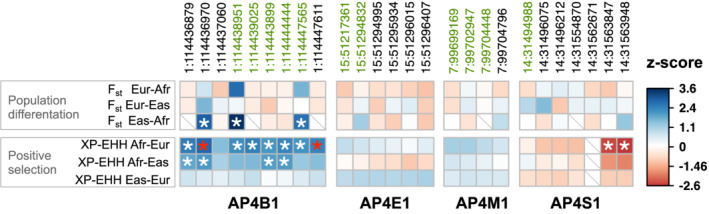
Exonic variants in AP‐4 genes exhibit evidence for recent population differentiation and positive selection. We tested variants in exons of any transcript of AP‐4 genes for evidence of evolutionary signatures of population differentiation (FST) and recent positive selection (XP‐EHH) within the 1,000 Genomes superpopulations (Methods). For a given evolutionary measure (rows) and exonic variant (columns, chromosome:position in hg19/GRCh37), the observed value was compared to a matched background distribution to derive a z‐score (indicated by the color of square per cell) and calculate an empirical p‐value. A positive (blue) or negative (red) z‐score indicates an increased or decreased value, respectively, compared to median value derived from matched background regions. Nominally significant (p < .05) and Bonferroni‐corrected statistically significant variant‐evolutionary measure pairs are denoted by white and red asterisks, respectively. Cells with missing data are indicated by a gray diagonal slash. Variants colored in green are classified “benign” by ClinVar. All exonic variants present in the SNPSNAP database and for which we could calculate a value for FST and XP‐EHH (see Methods) are shown. Overall, these data indicate AP4B1 exhibits differences among human populations and has undergone positive selection in African populations. AP‐4, adapter protein complex 4
