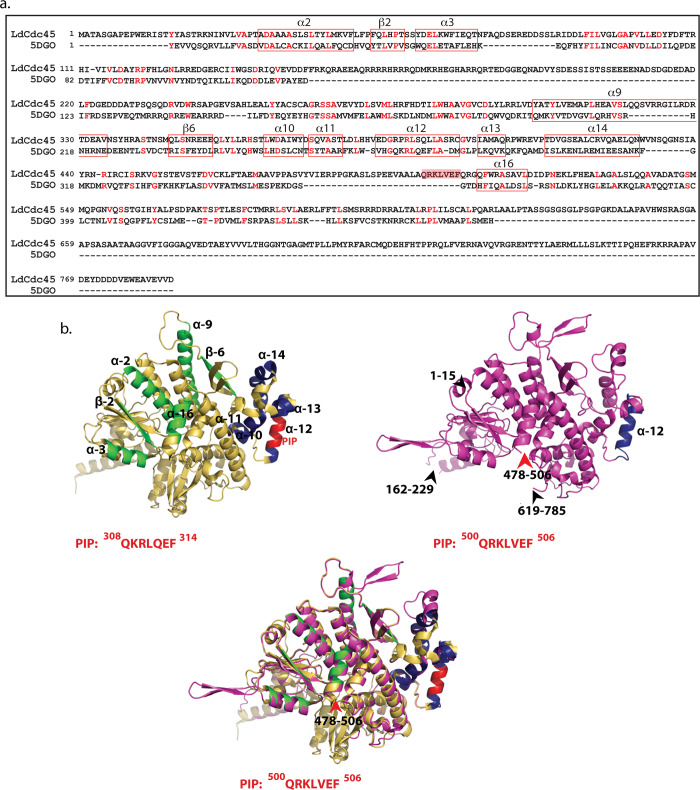
Fig 3. Structural analysis of Leishmania donovani Cdc45.
a. Sequence alignment of Leishmania donovani Cdc45 against human Cdc45 generated by Phyre2. Based on structural analysis of human Cdc45 by Simon et al [9], α10-α14 are helices that form the Mcm2/5 binding face. All other marked helices and β strands represent regions involved in interaction with GINS b. Upper left panel: Human Cdc45 ribbon representation derived from crystal structure (PDB ID: 5DGO) as reported by Simon et al [9]. Navy blue regions: Complex Interaction Domain (CID) that interfaces with Mcm2/5. Green regions: Domains that interface with GINS complex. Red region: PIP box. Sequence of PIP box indicated below structure. Upper right panel: Ribbon representation (magenta) of 3D model of Leishmania donovani Cdc45 modelled using Phyre2 against human Cdc45 (PDB ID: 5DGO) as template. Navy blue region indicates α12 helix. Black arrowheads and associated numbers indicate amino acid stretches that have been excluded by Phyre2 during modeling. Red arrowhead and associated numbers indicates location of PIP box (also excluded during modeling). Sequence of PIP box indicated below structure. Lower panel: View of superimposed structures of LdCdc45 and 5DGO, using PyMOL. Though showing overall structural similarity (RMSD value 2.2Å), the PIP motifs of the two structures do not overlap.