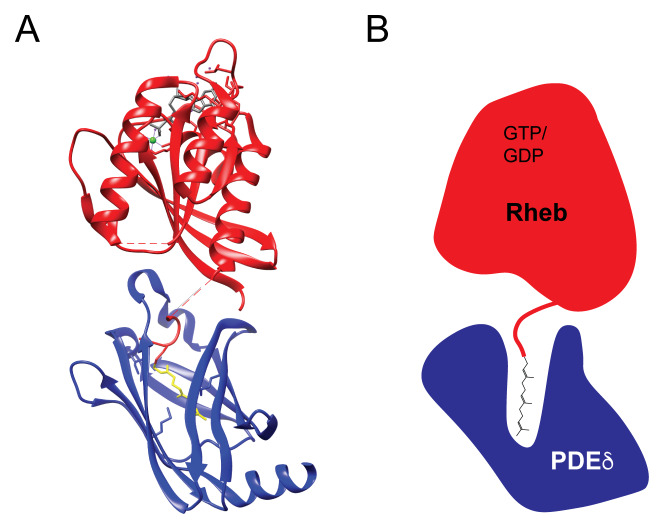
Figure 3. Rheb C-terminal farnesylation allows for interactions with PDEδ.
( A) A structure (3T5G) of the complex formed between Rheb (red) and PDEδ (blue) reveals that the interaction is largely independent of contacts between the Rheb and PDEδ proteins and is instead based on the insertion of the Rheb farnesyl group (yellow) deep into a hydrophobic cavity within PDEδ 91. Additional features include GDP bound to Rheb in gray, Mg2 + in green, and water molecules in purple. ( B) Schematic diagram of the Rheb–PDEδ heterodimer which highlights the insertion of the farnesyl group from Rheb deep into the hydrophobic cavity at the core of PDEδ. PDEδ, δ subunit of phosphodiesterase 6; Rheb, Ras homolog enriched in brain.