Figure 3. Pharmacologic targeting of PAI-1 inhibits macrophage invasion into atherosclerotic plaques without altering their SMC or collagen content.
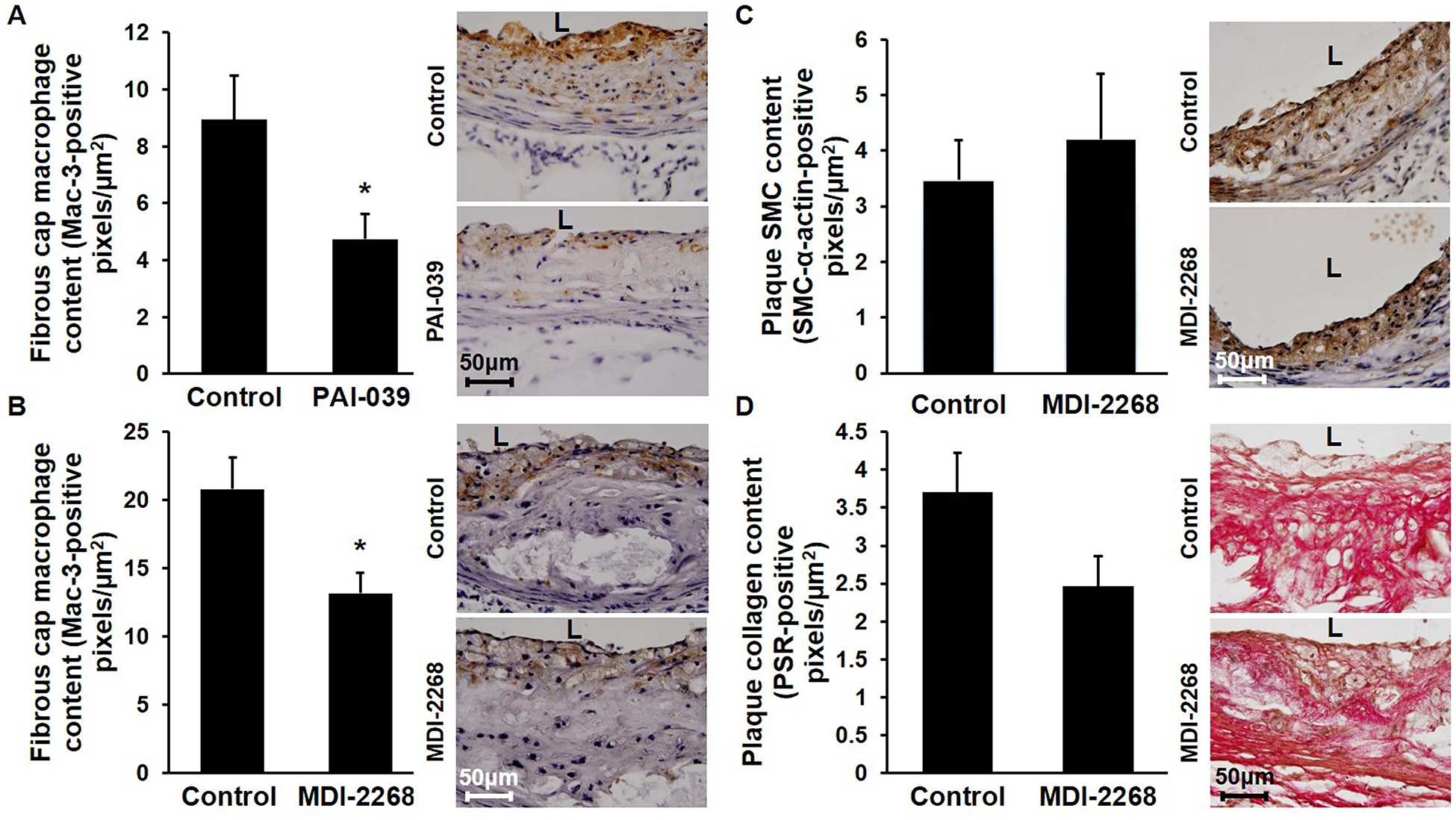
Ldlr−/− mice were fed WD containing or lacking PAI-1 inhibitor for 12 weeks, after which aortic root atherosclerotic plaque composition was assessed. (A) PAI-039 decreases fibrous cap macrophage content. Quantified data (n=5/group; *P<0.05) and representative images demonstrating macrophage invasion (brown color) are shown. (B) MDI-2268 decreases fibrous cap macrophage content. Quantified data (n=6–7/group; *P<0.05) and representative images are shown. (C) MDI-2268 does not significantly affect intimal SMC content, assessed by SMC-α actin immunostaining (brown color). Quantified data (n=4–6/group, difference between groups did not achieve statistical significance; P>0.6) and representative images are shown. (D) MDI-2268 does not significantly affect plaque collagen content, assessed by picrosirius red (PSR) staining. Quantified data (n=6–7/group, difference between groups did not achieve statistical significance; P>0.08) and representative images are shown. L, lumen.
