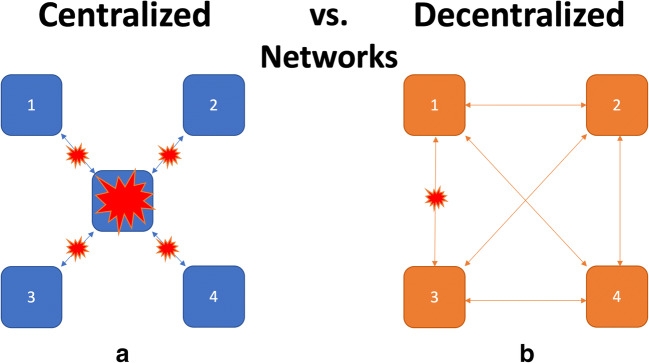
Fig. 2.
Centralized vs. decentralized networks. a Centralized networks have a single point of failure. If the central node goes down, the entire network becomes nonfunctional. All trust is placed in the central authority which is the arbiter of truth. b Decentralized networks do not have a single point of failure. If one or more nodes go down, there is sufficient redundancy that the remainder of the network remains functional. All the nodes must arrive at a consensus as to what the truth is