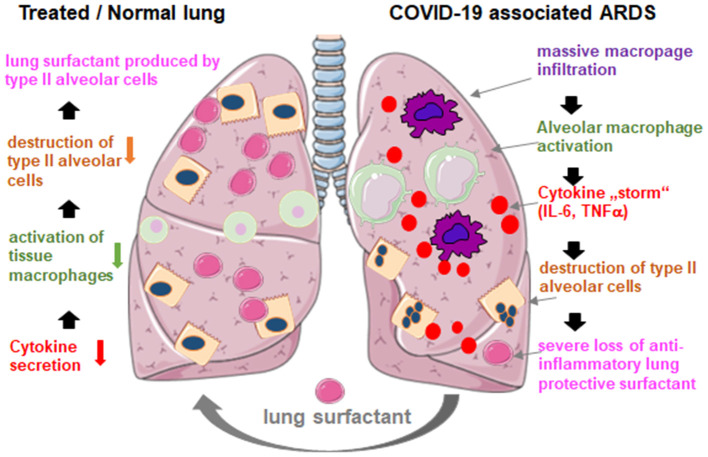
Figure 2.
Hypothetical mechanism of externally applied lung surfactant for pulmonary protection in severe COVID-19 associated ARDS. COVID-19 associated ARDS is characterized by massive macrophage infiltration, tissue alveolar macrophage activation and a potentiation of cytokine production in the lung (cytokine “storm”), which leads to the destruction of surfactant producing type II alveolar cells, which worsens the situation through the loss of anti-inflammatory, anti-fibrotic lung surfactant. Exogenous surfactant may reduce inflammation and thus restore pulmonary survival. Created using smart servier medical art under https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/.