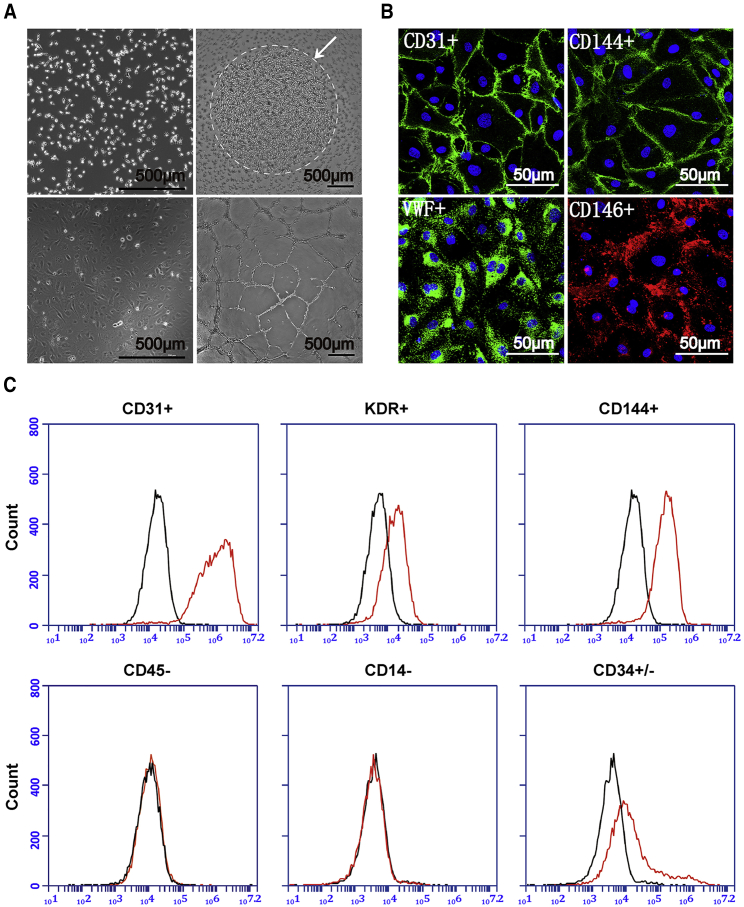
Figure 1.
Generation and Phenotypic Identification of EPCs from Human Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells
(A) Morphology of (upper left) mononuclear cells 24 h after inoculation. EPCs colonies formed (upper right) after 10–14 days culture. After passaging, the predominant cell type exhibits a cobble stone morphology (lower left) and is able to form endothelial cell-like networks in vitro (lower right). Scale bar, 500 μm. (B) Immunostaining assay of EPCs in vitro, CD31 (green; DAPI, blue), CD144 (green; DAPI, blue), vWF (green; DAPI, blue), and CD146 (red; DAPI, blue); Scale bar, 50 μm. (C) Flow cytometric analysis of L-EPCs in vitro. The red lines represent the L-EPCs labeled with different antibodies. The black lines denote the negative control.