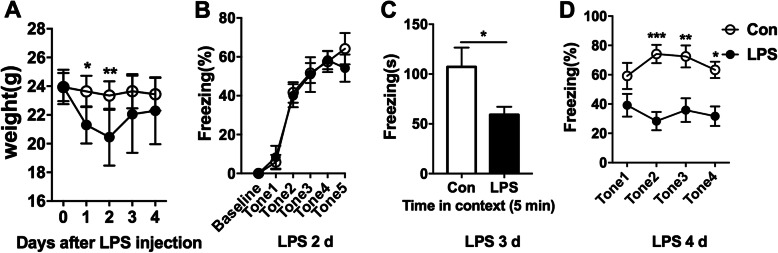
Fig. 1.
Impaired cognitive dysfunction after lipopolysaccharide (LPS) injection. Mice were i.p. injected with LPS (5 mg kg−1) and behavior tests were conducted at 1 day after LPS injection. a There was a reduction in body weight between saline-treated and LPS-injected mice. n = 8 each group. The data was analyzed by repeated measures ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. b LPS injection did not affect acquisition of fear conditioning test in mice. n = 8 each group. c,d Decreased freezing time in (c) contextual and (d) cued fear conditioning test in LPS-treated mice indicated that 5 mg kg−1 LPS peritoneal injection induced cognitive dysfunction in mice. n = 8 each group. Data c was analyzed by unpaired T test and data b and d were analyzed by repeated measures ANOVA followed by Bonferroni post hoc test, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. Con = saline injected control. LPS = i.p. LPS injection. i.p. = intraperitoneal