Figure 6. Compartmentalized NAD+ synthesis coordinates glucose metabolism and transcription.
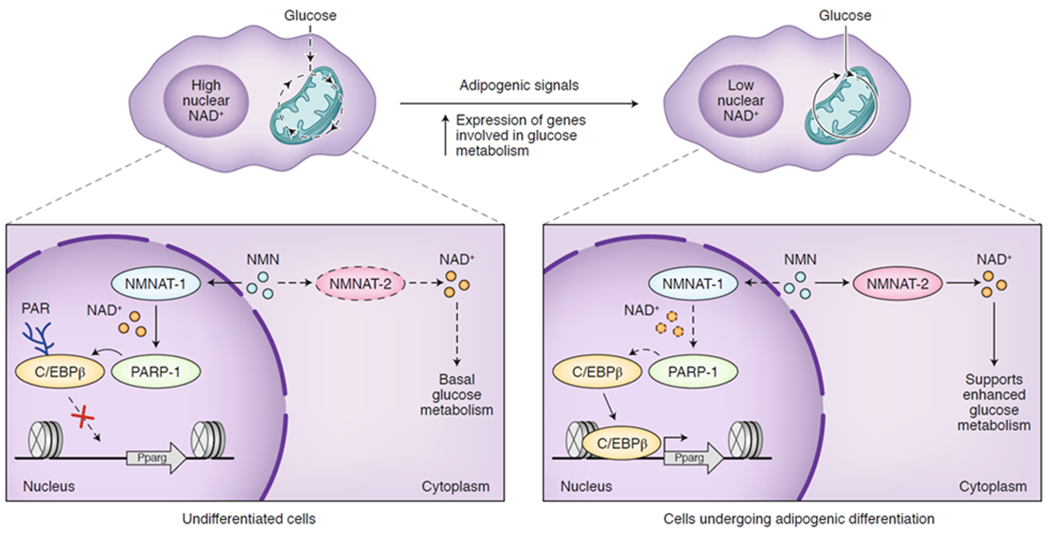
In an undifferentiated state (left), NMN is used by the nuclear NMNAT-1 to produce NAD+, promoting PARP1-dependent ADP-ribosylation of the transcription factor C/EBPβ to hold the cell in this undifferentiated state. Once proper adipogenic signals are received (top), cytoplasmic NMNAT-2 is induced to produce NAD+ for glycolysis, depleting the nuclear NAD+ pool and initiating C/EBPβ-mediated adipogenic differentiation (right). PARP1 = poly-ADP-ribose polymerase 1, C/EBPβ = CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein β, NMN = nicotinamide mononucleotide, NMNAT = nicotinamide mononucleotide adenylyltransferase, Pparg = peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma.
