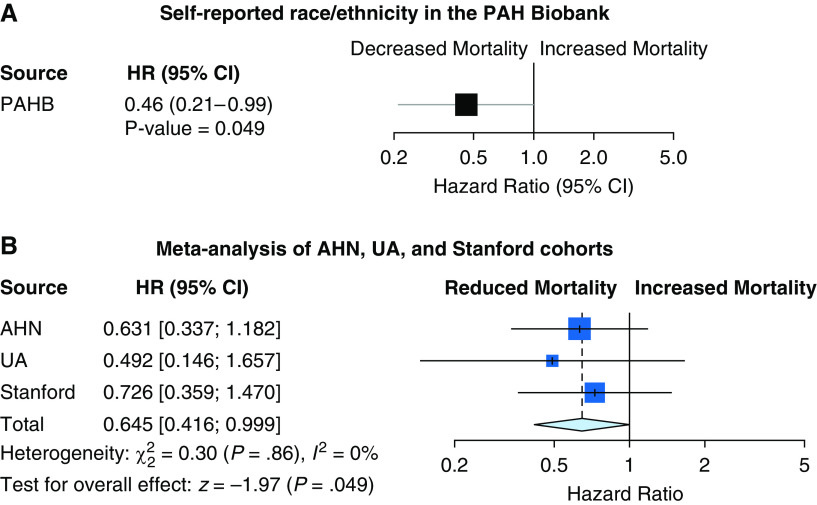
Figure 3.
All-cause mortality hazard ratios for self-reported race/ethnicity in the (A) Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension (PAH) Biobank and in (B) validation meta-analysis of the AHN, UA, and Stanford cohorts. Cox proportional hazards regression for all-cause mortality was performed in idiopathic PAH (PAH Biobank) and patients with Group 1 PAH (AHN, UA, and Stanford cohorts), adjusted for age, sex, prostacyclin use, and log (pulmonary vascular resistance). The Stanford cohort analyses did not adjust for prostacyclin use because these newly diagnosed patients were treatment naive. Patients with Hispanic ethnicity were compared with non-Hispanic white patients. Meta-analysis of Cox proportional hazards regression used a fixed effects model, and inverse SE was used as a weight for each study. AHN = Allegheny Health Network; CI = confidence interval; HR = hazard ratio; PAHB = Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension Biobank; UA = University of Arizona.