Figure 7.2.
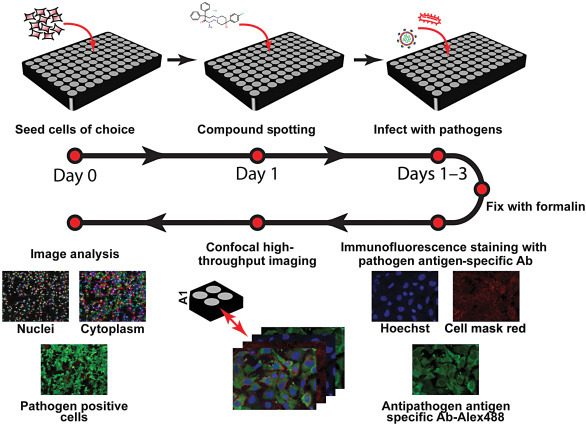
Phenotypic screening using high-throughput HCI.
Cells susceptible to the pathogen of interest are seeded in HCI plates. Next day, cells are pretreated with appropriate concentration of the compounds and then infected with the pathogen of interest for optimal time wherein 70%–80% infection results. The infected plates are then submerged in 10% formalin for 24 h to inactivate the pathogen and to fix the cells. Immunofluorescence staining is then performed, using a primary antibody specific to a pathogen antigen, and an appropriate fluorescence-labeled secondary antibody. Dyes such as cell mask red and Hoechst are added to detect the cell cytoplasm and nuclei, respectively. Automated image acquisition and analysis is performed and data are analyzed using Columbus software to quantitate the percentage of inhibition of pathogen infection and loss in cell number that represents cellular toxicity, in the presence of the compound [39]. HCI, high-content imaging.
