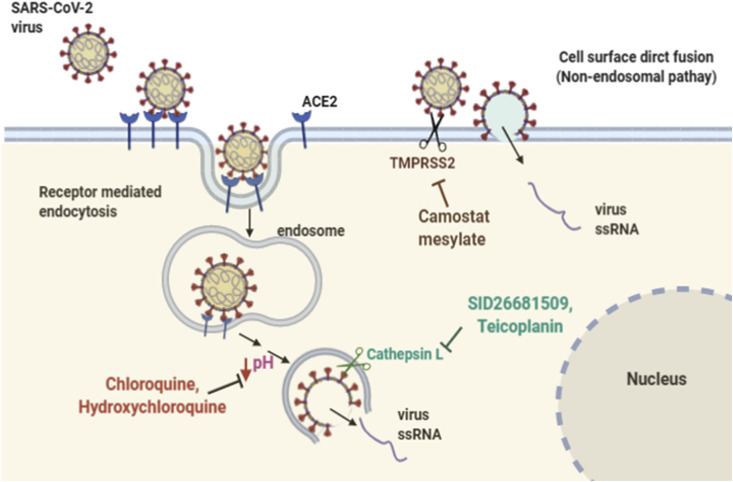
Fig. 2.
Routes of SARS-CoV-2 virus entry into target cells. Binding of a viral (S) glycoprotein to ACE2 receptor can be followed by receptor mediated endocytosis, which ends up in endosomal compartment, where an increase in H+ influx into the endosome activates cathepsin L which activates viral (S) glycoprotein and facilitates viral membrane fusion and releases of ssRNA out of the endosome (left). Chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine are known to block virus infection mainly by increasing endosomal pH required for virus/cell fusion. The thiocarbazate SID26681509 and teicoplanin are inhibitors of cathepsin L. Alternatively, proteolytic cleavage of the viral (S) protein by TMPRSS2 protease on the surface of host cell can induce direct fusion of the viral and plasma membrane leading to release of the viral ssRNA into the cytoplasm (right). The camostat mesylate drug inhibits TMPRSS2 activity.