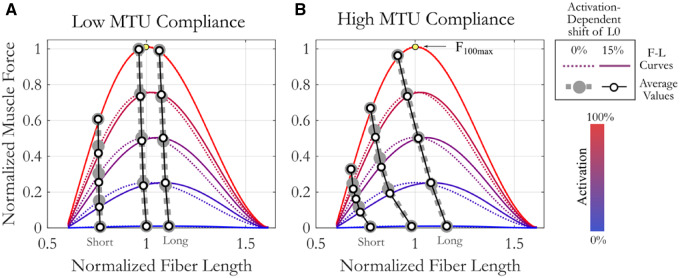
Fig. 4.
The influence of compliance level (low [A], high [B]) on average muscle operating length and force capacity across activation levels. On average, muscle length decreases with increasing activation and is significantly influenced by interactions between starting length, compliance, and activation level. Muscles with low MTU compliance (A) change length with activation less than muscles with high compliance (B). While activation-dependent shifts in L0 change operating length (difference between hollow and filled circles), they are not significant. F–L curves at five different activation levels are distinguished by color (blue: low activation, red: high activation). Line type designates presence (solid) or absence (dashed) of activation-dependent shift in L0. Circles represent the mean value at the five different activation levels for muscle models with (hollow) or without (filled) activation-dependent shift in L0. L0100 is always a normalized fiber length of 1. Yellow circle marks the maximum force at 100% activation, F100max.