Fig. 1.
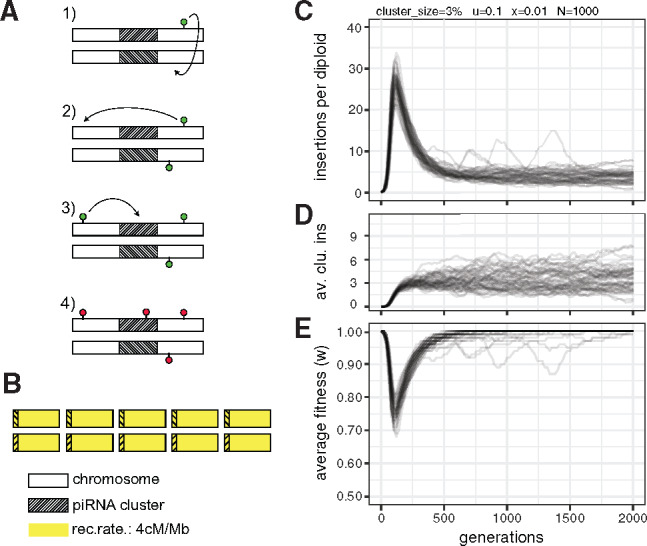
—Dynamics of TE invasions with piRNA clusters and deleterious TE insertions. (A) Under the trap model, the proliferation of an active TE (green) is stopped when one copy jumps into a piRNA cluster (i.e., the trap; hatched area), which deactivates all TE copies in trans (red). (B) We simulated five chromosomes with a size of 10 Mb for a diploid organism. A piRNA cluster was simulated at one end of each chromosome and a recombination rate of 4 cM/Mb was used. (C) The abundance of TE insertions during an invasion. Fifty replicates are shown. (D) Number of cluster insertions per diploid during an invasion (av. clu. ins). (E) Average fitness during an invasion.
