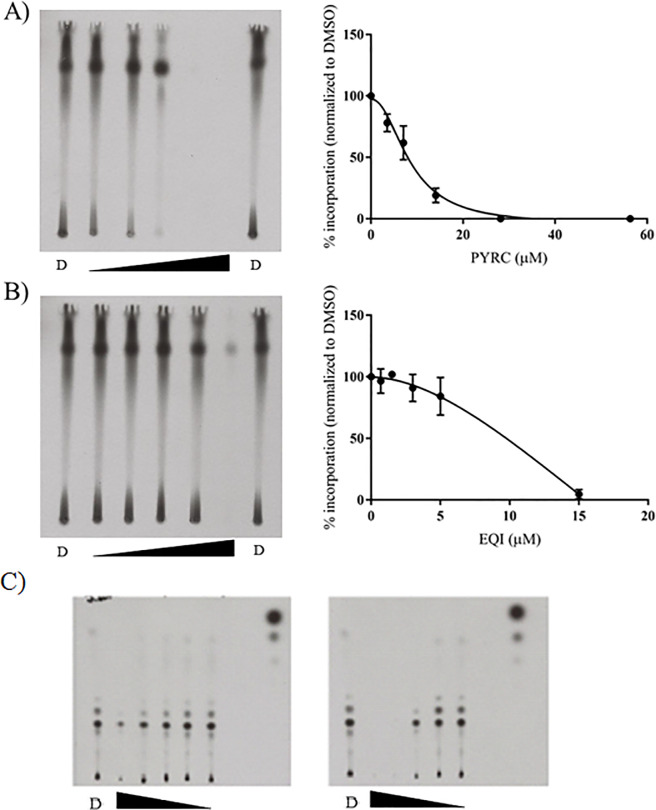
Fig 6. PYRC and EQI impair [1-14C] acetate incorporation in S. aureus.
S. aureus was incubated with [1-14C] acetate (4μCi/mL) for 2 hours in the presence of DMSO, PYR or EQI. A) left panel, representative X-ray film of lipid extract from S. aureus following PYRC treatment eluted on a reverse-phase TLC plate. DMSO control indicated as “D”. The triangle indicates an increase in drug concentration from left to right. Right panel, percent incorporation of [1-14C] acetate following PYRC treatment normalized to DMSO. Mean data of two independent experiments are shown ± standard error of the mean. B) Left panel, representative X-ray film of lipid extract from S. aureus following EQI treatment eluted on a reverse-phase TLC plate. DMSO control indicated as “D”. The triangle indicates an increase in drug concentration from left to right. Right panel, percent incorporation of [1-14C] acetate following EQI treatment normalized to DMSO. Mean data of two independent experiments are shown ± standard error of the mean. C) Representative X-ray film of lipid extract from S. aureus following PYRC and EQI treatment eluted on a normal-phase TLC plate. DMSO control indicated as “D”. The triangle indicates a decrease in drug concentration from left to right. Tested concentrations of EQI: 0.7, 1.5, 3, 5, and 15 μM; PYRC 3.5, 7, 14, 28, and 56 μM. Left panel, percent incorporation of [1-14C] acetate following EQI treatment normalized to DMSO. Right panel, percent incorporation of [1-14C] acetate following PYRC treatment normalized to DMSO.