Fig. 2. Test of nonfouling property, immunomodulatory effect, and phagocytosis.
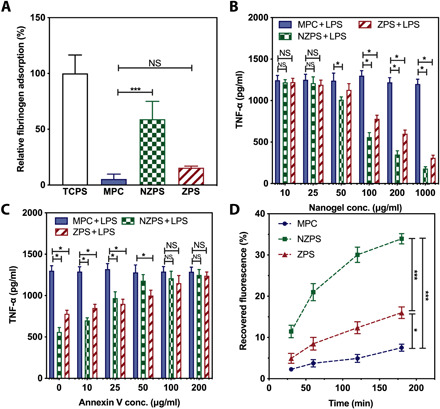
(A) Fibrinogen adsorbed onto TCPS, MPC, NZPS, and ZPS hydrogel surfaces measured by ELISA. (B) RAW 264.7 macrophages (105 per well) were treated with the MPC, NZPS, or ZPS nanogels at various concentrations (10, 25, 50, 100, 200, and 1000 μg/ml) for 18 hours followed by the stimulation of LPS (100 ng/ml) for 48 hours. The level of TNF-α secretion in the supernatant was measured by an ELISA kit. (C) The MPC, NZPS, or ZPS nanogels (100 μg/ml) were preincubated with an annexin V solution at various concentrations (0, 10, 25, 50, 100, and 200 μg/ml) for 6 hours. RAW 264.7 macrophages (105 per well) were then treated with these nanogels (100 μg/ml) for 18 hours followed by the stimulation of LPS (100 ng/ml) for 48 hours. The level of TNF-α secretion in the supernatant was measured by the ELISA kit. (D) RAW 264.7 macrophages (105 per well) were incubated with MPC, NZPS, or ZPS nanogels encapsulating FITC-BSA for 30, 60, 120, and 180 min, after which the cells were washed and lysed for the detection of recovered fluorescence. Statistical significance was determined using Student’s t test. NS, no significance. *P < 0.05 and ***P < 0.001. Data are represented as mean ± SEM.
