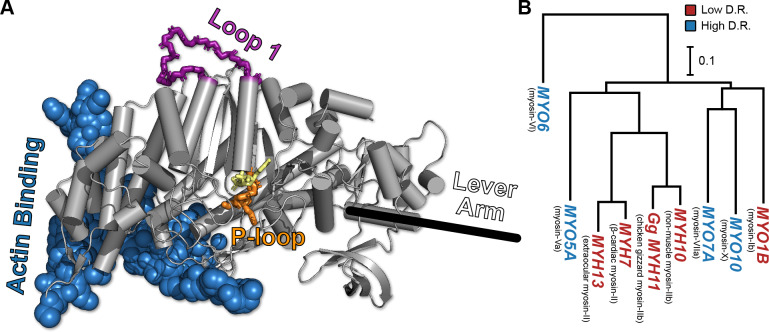
Figure 1. The conserved myosin motor domain fold across a diverse phylogeny of motors.
(A), A crystal structure (PDB ID 4PA0) (Winkelmann et al., 2015) of Homo sapiens β-cardiac myosin motor domain as an example of the conserved myosin motor domain fold. We note the structural elements most relevant to our work here (loop 1, in purple backbone sticks, and the P-loop, in orange sticks), along with the actin binding region (blue spheres). For orientation, we include the location of the lever arm (black line) and, to indicate the active site, the estimated location of ADP (yellow sticks). (B) The phylogenetic relationship the various myosin motor domains examined in this work. Except MYH11, all genes are from Homo sapiens. Gene names in blue indicate high duty ratio motors and red indicates low duty ratio. Common protein names are indicated as parentheticals to the left of each gene name. Phylogenetic relationships were inferred from the sequence of the motor domain using k-mer distances (Edgar, 2004a).