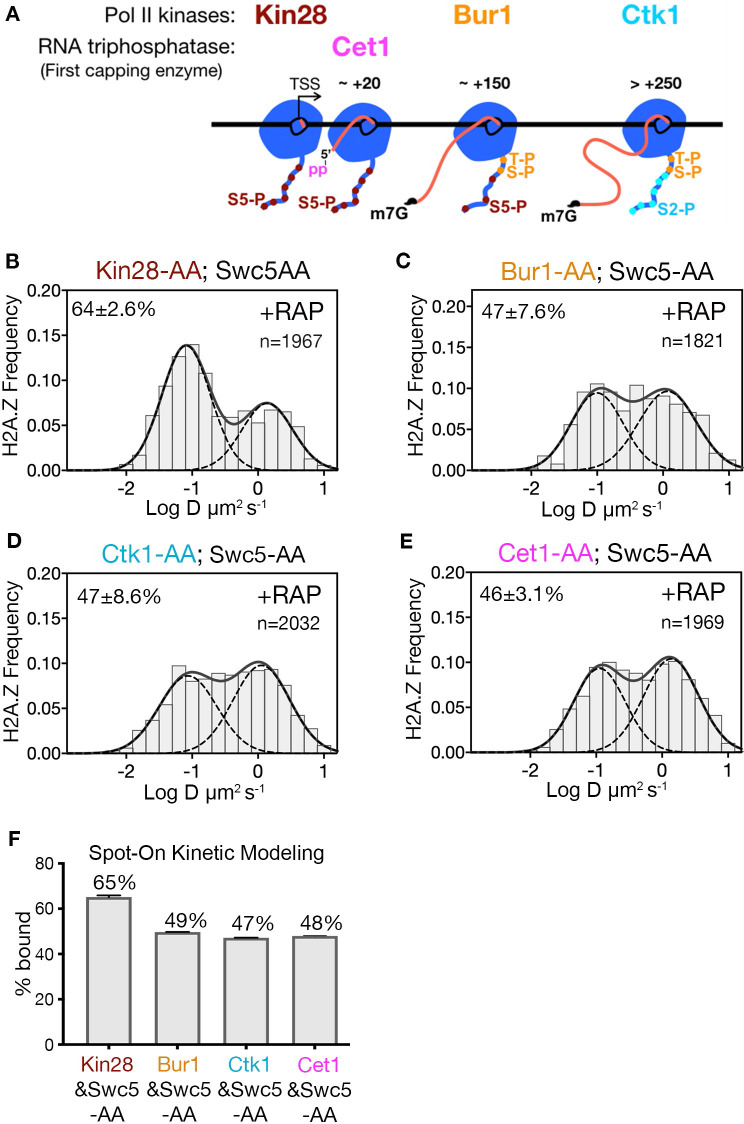
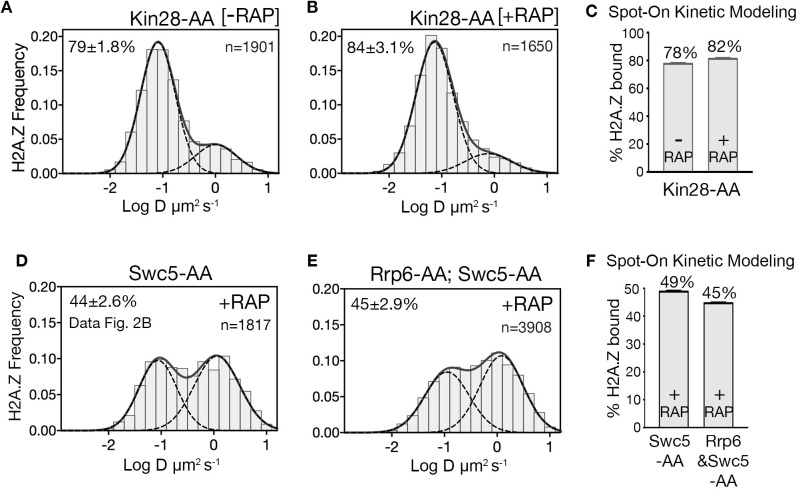
Figure 4. Kin28 phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II CTD is critical for H2A.Z eviction.
(A) Schematic representation shows the three Pol II kinases Kin28, Bur1 and Ctk1 recruited at initiation, early-elongation and elongation phases respectively of Pol II and corresponding phosphorylation of indicated Rpb1 CTD sites. Set1 is the first of the three RNA capping enzymes; it removes γ-phosphate from the RNA 5’end to generate 5’ diphosphate. (B, C, D, E) Normalized histograms and two-component Gaussian fits for H2A.Z-Halo imaged in cells co-depleted for Swc5 along with Kin28 (B), Bur1 (C), Ctk1 (D) and Cet1 (E). (F) Spot-On results show Kin28 is required to evict H2A.Z. All molecules tracked with JF552 dye.