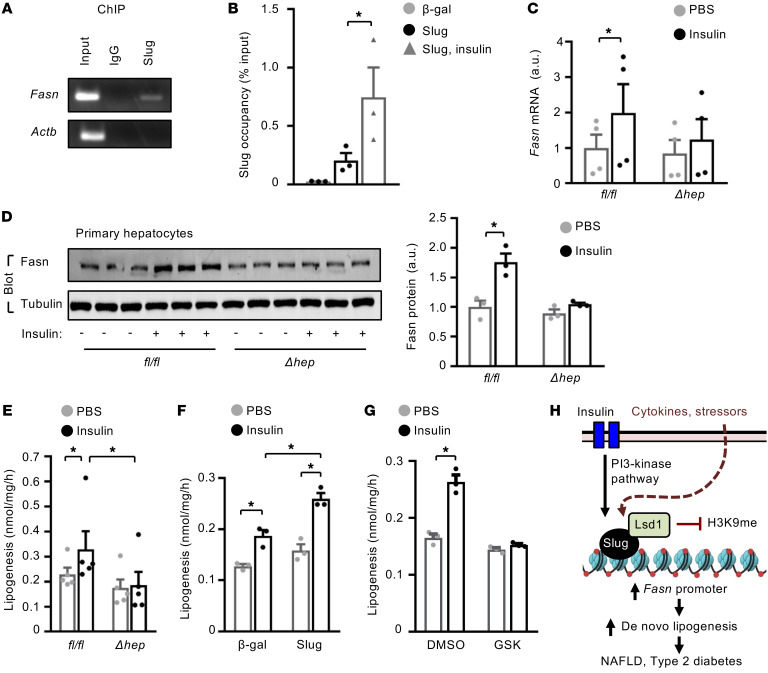
Figure 7. Insulin stimulated lipogenesis via Slug/Lsd1 epigenetic pathway.
(A and B) Primary hepatocytes were transduced with Slug or β-gal adenoviral vectors, and stimulated with insulin (100 nM for 2 hours). Slug occupancy on the Fasn promoter was assessed by ChIP-qPCR and normalized to inputs (n = 3 per group). (C–E) Primary hepatocytes were stimulated with insulin (50 nM) for 3 hours (C) or 12 hours (D and E). (C) Fasn mRNA abundance (normalized to 36B4 levels) (n = 3 per group). (D) Cell extracts were immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. Fasn levels were normalized to α-tubulin levels. (E) Lipogenesis rates (n = 3 per group). (F) Lipogenesis (normalized to protein levels, n = 3 per group). Primary hepatocytes were transduced with Slug or β-gal adenoviral vectors and stimulated with insulin (50 nM for 12 hours). (G) Lipogenesis (n = 3 per group). Primary hepatocytes were pretreated with GSK2879552 (4 μM) or DMSO and stimulated with insulin (50 nM for 5 hours). (H) Insulin stimulates Slug expression, Slug-Lsd1 interactions, and recruitment of Slug/Lsd1 to the Fasn promoter where Lsd1 demethylates H3K9, thereby activating Fasn expression and de novo lipogenesis. Cytokines and metabolic stressors similarly activate the Slug/Lsd1 lipogenic pathway. Data are presented as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, 1-way ANOVA/Sidak posttest.