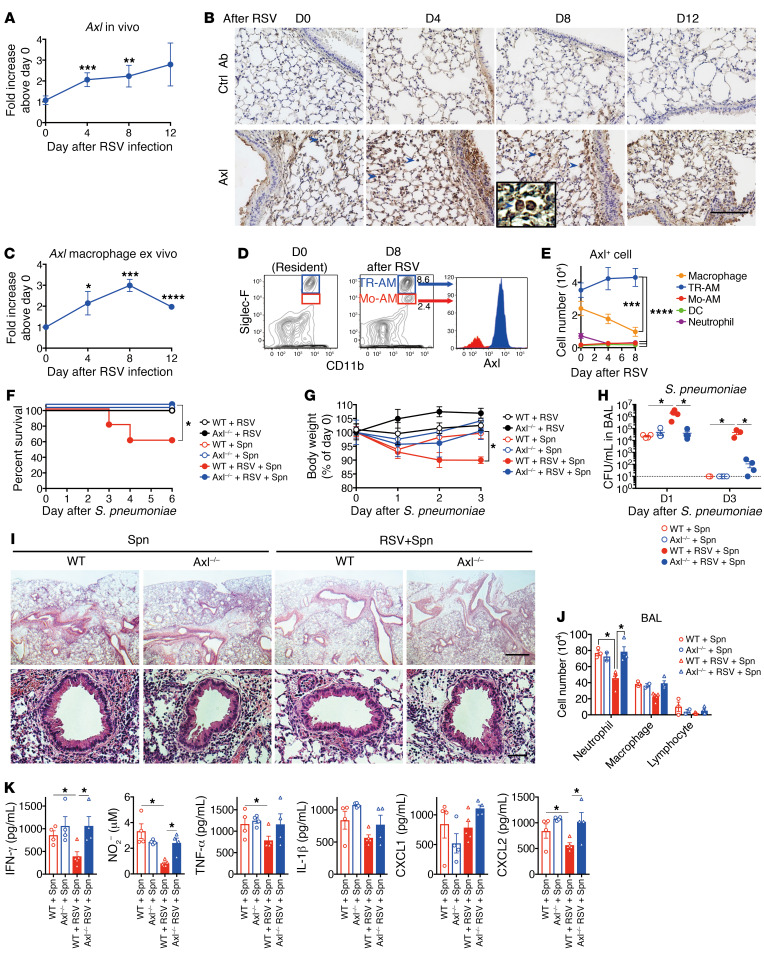
Figure 3. Axl is involved in promoting susceptibility to S. pneumoniae after RSV infection.
(A) Axl levels in whole lung from an RSV-infected WT mouse. (B) Immunohistochemical analysis (DAB) of Axl in the lung tissue sections from naive (D0) and RSV-infected mice. Blue arrows indicate Axl+ macrophages. Scale bar: 200 μm. (C) Axl expression in the alveolar macrophages isolated from naive and RSV-infected mice on days 4, 8, and 12 after infection. (D) Axl expression in the tissue-resident alveolar macrophages (TR-AM) and monocyte-derived alveolar macrophages (Mo-AM) from naive and RSV-infected mice at day 8 after RSV infection. (E) Temporal changes in the number of Axl+ cells after RSV infection. (F) Changes in the survival rate and (G) body weight of RSV-infected WT or Axl–/– mice after S. pneumoniae infection. (H) Titers of S. pneumoniae in the BAL fluid from RSV-infected mice on days 1 and 3 after S. pneumoniae infection. (I) Representative H&E-stained lung tissue sections on day 1 after S. pneumoniae infection. Scale bars: 200 μm (upper), 50 μm (lower). (J) The number of neutrophils, macrophages, and lymphocytes in the BAL fluid on day 1 after S. pneumoniae infection. (K) The levels of IFN-γ, NO, TNF-α, IL-1β, CXCL1, and CXCL2 in the BAL fluid from WT and Axl–/– mice on day 1 after S. pneumoniae infection. The data are expressed as mean ± SEM; n = 10 (F and G), n = 4–5 (except for F and G). Representative results from 2 independent experiments are shown. The following statistical tests were used: One-way ANOVA (A, E, G, H, J, and K) and Gehan-Breslow-Wilcoxon test (F). *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.