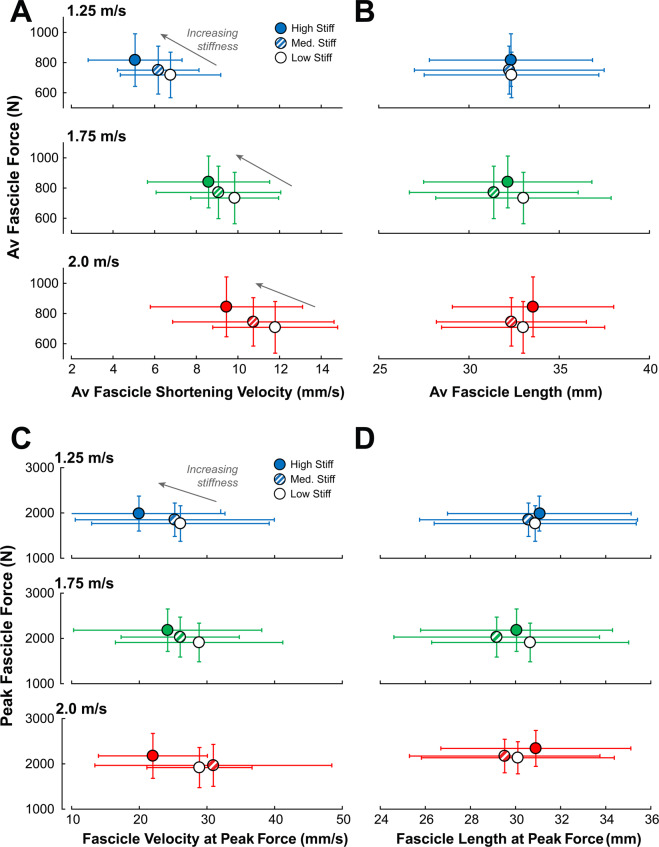
Figure 8.
Added foot stiffness shifts Soleus muscle Force-velocity operating region. Stance-averaged Soleus fascicle force data were plotted as a function of: (A) average fascicle shortening velocity during stance and (B) average fascicle length during stance. The peak Soleus fascicle force data were also plotted as a function of: (C) fascicle shortening velocity at the time of peak force, and (D) fascicle length at the time of peak force. Added foot stiffness was able to increase Soleus force output without added muscle activation (Fig. 6 and Supplementary Fig. 10), suggesting that the increased force was primarily due to a shift in the force-velocity operating region. Error bars signify s.d. between subjects.