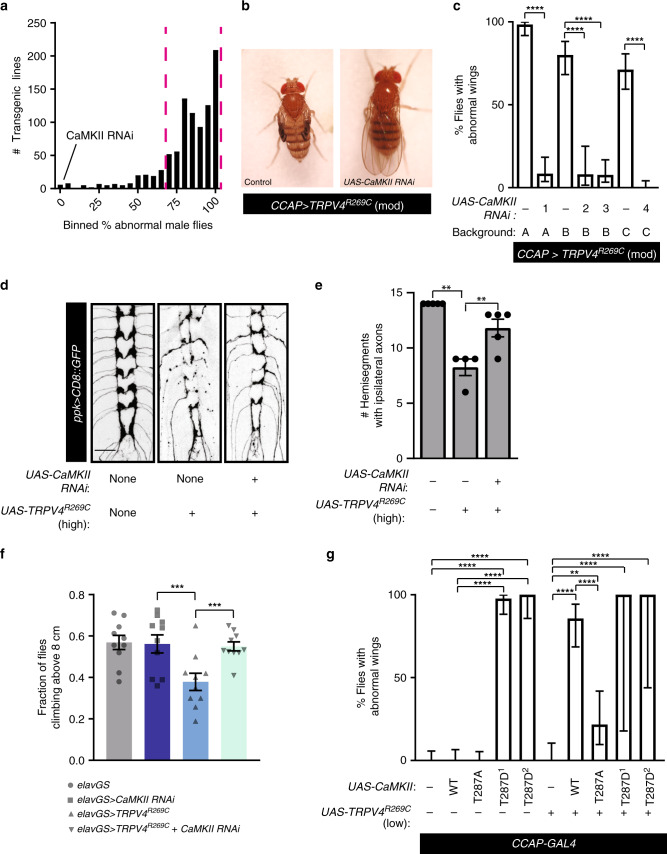
Fig. 3. CaMKII is required for TRPV4R269C-mediated neuronal toxicity.
a Histogram of results from genetic modifier screen against TRPV4R269C toxicity in NCCAP. Dashed magenta lines denote upper and lower bounds of control lines. b Images of flies expressing TRPV4R269C(mod) ± CaMKII RNAi. c Percentage ± 95% CI of flies with unexpanded wings when co-expressing TRPV4R269C(mod) and different CaMKII RNAi fly lines. A = TRiP collection lines, B = Vienna GD collection lines, and C = Vienna KK collection lines. From left to right n = 65, 59, 60, 25, 65, 66, and 90 flies. Χ2 test of all groups (p < 0.0001) followed by pairwise two-sided Fisher’s exact test. d Confocal stacks of axonal projections in C4da neurons expressing TRPV4R269C(high) ± CaMKII RNAi. e Mean ± SEM innervation in d. n = 5, 4, and 5 larvae, respectively. One-way ANOVA (p < 0.0002), Tukey’s post hoc test. Scale bar, 25 µm. f Climbing performance of flies 7 days after induction of expression of TRPV4R269C(high) ± CaMKII RNAi with 200 μM RU486. Mean ± SEM. n = 10 vials of 10 flies per genotype. Two-way ANOVA (p < 0.0001), Tukey’s post hoc test. g Percentage ± 95% CI of flies with unexpanded wings when co-expressing TRPV4R269C(low) with variants of CaMKII. T287D1 and T287D2 denote independent UAS-CaMKIIT287D lines. From left to right n = 63, 55, 68, 44, 23, 33, 28, 23, 2, and 3 flies. Χ2 test of all groups (p < 0.0001) followed by pairwise two-sided Fisher’s exact test. For all panels: **p < 0.01, ****p < 0.0001.