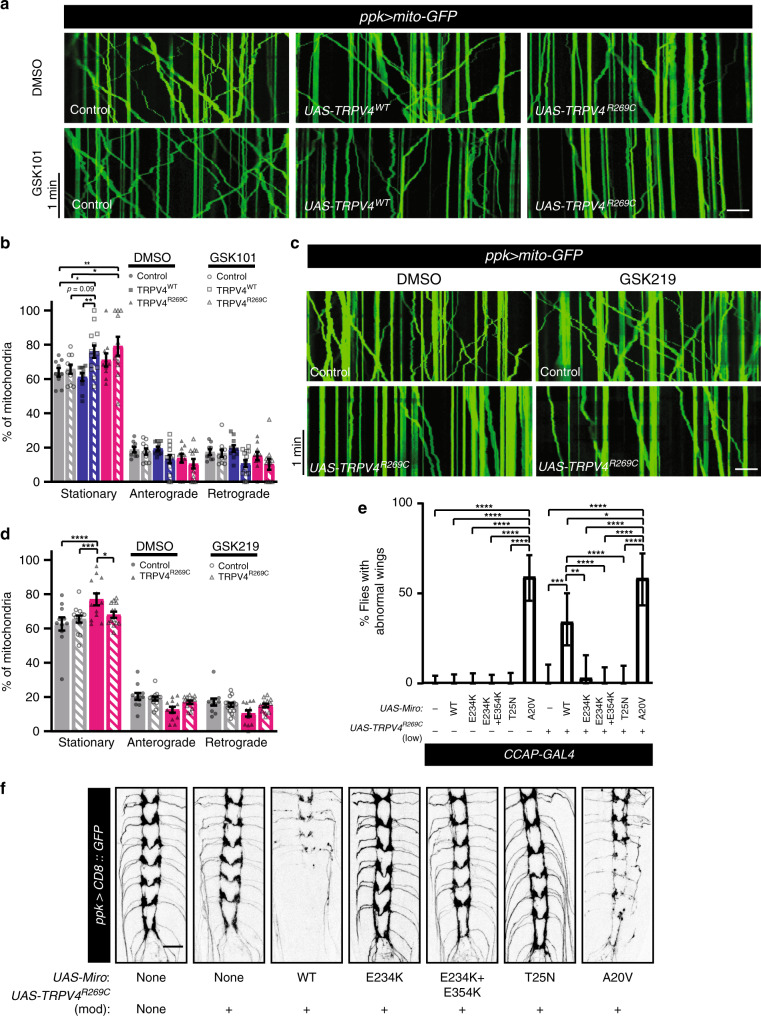
Fig. 7. Pharmacologic manipulation of TRPV4 modulates mitochondrial transport and the mitochondrial transport protein Miro enhances TRPV4R269C-mediated toxicity.
a Kymographs of mito-GFP transport in C4da neuron proximal axons in larvae expressing no TRPV4, TRPV4, or TRPV4R269C treated with 40 nM GSK101 or DMSO. Scale bar, 10 μm. b Fraction of stationary, anterograde-, and retrograde-moving mitochondria from a. Mean ±SEM. For control, TRPV4WT, and TRPV4R269C: DMSO n = 9, 10, 10 larvae; GSK101 n = 10, 14, 11 larvae. Two-way ANOVA (p < 0.0001), Tukey’s post hoc test. c Kymographs of mito-GFP transport in C4da neuron axons in larvae expressing no TRPV4 or TRPV4R269C raised on food containing DMSO or 100 µM GSK219 and treated with 10 µM GSK219 during imaging. Scale bar, 10 μm. d Percentage of stationary, anterograde-, and retrograde-moving mitochondria from c. Mean ± SEM. For control and TRPV4R269C: DMSO n = 11 and 12 larvae; GSK219 n = 14 and 13. Two-way ANOVA (p < 0.0001), Tukey’s post hoc test. e Percentage ± 95% CI of flies with unexpanded wings when expressing Miro variants ± TRPV4R269C(low) in NCCAP. From left to right n = 86, 72, 64, 77, 62, 54, 33, 38, 32, 39, 35, and 41 flies. Χ2 test (p < 0.0001) followed by pairwise two-sided Fisher’s exact test. f Representative confocal images of C4da neuron projections in larvae expressing TRPV4R269C(mod) (as in Supplementary Fig. 2d and e) ± overexpressed Miro variants. Similar results observed in all imaged larvae within each genotype (n = 7, 8, 8, 8, 7, 8, and 8 larvae from left to right) Scale bar, 25 μm. For all panels: *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, ****p < 0.0001.