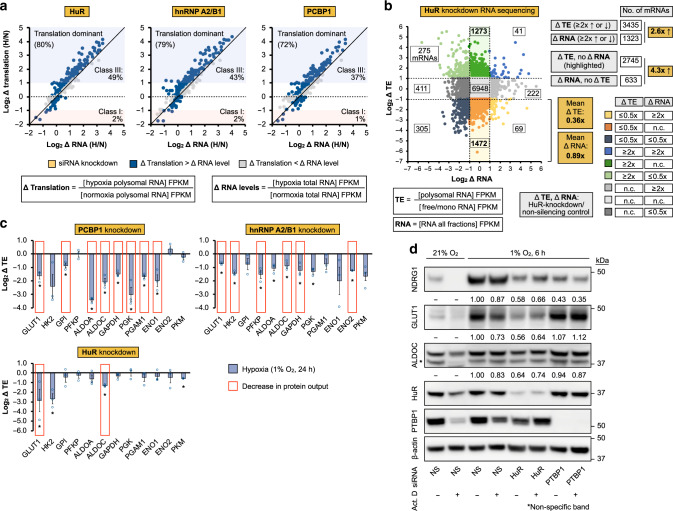
Fig. 4. Hypoxia-adaptive RBPs promote glycolytic induction through translation efficiency.
a Mechanism of hypoxic induction for RBP-dependent translatomes. Global analysis of hypoxia-induced translational versus RNA-level changes in U87MG using RNA sequencing of ribosome density fractions for HuR-, hnRNP A2/B1-, and PCBP1-dependent targets. Color scheme: red, Class I proteins, normoxia-enriched; blue, Class III proteins, hypoxia-enriched. b Global analysis of HuR-dependent changes in mRNA translation efficiency and steady-state expression in U87MG using RNA sequencing of ribosome density fractions following siRNA-mediated HuR-silencing. c Hypoxic translation efficiency regulation of glycolytic effectors by the hypoxia-adaptive RBPs PCBP1, hnRNP A2/B1, and HuR, as determined by qRT-PCR of ribosome density fractions. Asterisk denotes statistical significance calculated using two-sided Student’s t-tests compared to non-silencing control. Exact p values: PCBP1 siRNA: GLUT1 (p = 0.02), GPI (p = 0.03), ALDOA (p = 0.001), ALDOC (p = 0.02), GAPDH (p = 0.007), PGK (p = 0.03), PGAM1 (p = 0.004), ENO1 (p = 0.047); hnRNP A2/B1 siRNA: GLUT1 (p = 0.007), HK2 (p = 0.004), PFKP (p = 0.04), ALDOA (p = 0.04), ALDOC (p = 0.048), GAPDH (p = 0.05), PGK (p = 0.03), ENO2 (p = 6.79e−05); HuR siRNA: GLUT1 (p = 0.04), HK2 (p = 0.04), ALDOC (p = 0.001), PKM (p = 0.0008). Data represent mean ± SEM (error bars) of three independent experiments (n = 3). Red box: observed decrease in protein output as determined by TMT-pSILAC. d Representative immunoblots of normoxic and hypoxic (6 h) U87MG treated with actinomycin D (+) or vehicle DMSO (−). NS: non-silencing. Quantitation represents mean of three independent experiments (n = 3). Source data are provided as a Source data file.