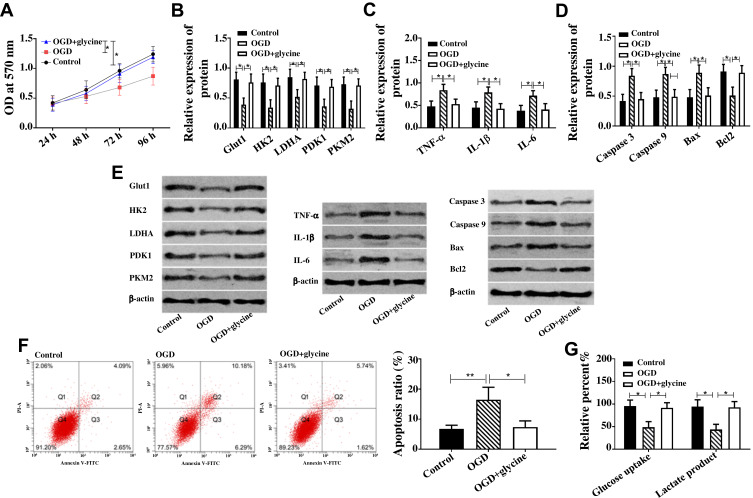
Figure 1.
Glycine inhibited cell apoptosis, glucose metabolism disorder and inflammatory response.
Notes: (A) Glycine improved cell activity of ischemic stroke when * was 96 h, P<0.05. (B) Glycine up-regulated Glut1, HK2, LDHA, PDK1, PKM2 in ischemic stroke. (C) Glycine down-regulated TNF-α, IL-1βI and L-6 in ischemic stroke. (D) Glycine down-regulated Caspase 3, Caspase 9, Bax and up-regulated Bcl2 in ischemic stroke. (E) Western blot band of protein; Glycine up-regulated Caspase 3, Caspase 9, Bax and Bcl2 in ischemic stroke. (F) Glycine reduced apoptosis of ischemic stroke. (G) Glycine increased glucose intake and formation amount of lactic acid in ischemic stroke. *P<0.05, **P<0.01. The experiments were repeated for three times.
Abbreviations: OD, optical density; Glut1, Glucose transporter type 1; PKM2, Pyruvate Kinase M2; HK2, Hexokinase 2; LDHA, Lactate Dehydrogenase A; PDK1/2, Pyruvate Dehydrogenase Kinase ½; TNF-α, Tumor Necrosis Factor α; IL-1β, interleukin-1β; IL-6, interleukin-6; Bax, BCL2 Associated X, Apoptosis Regulator; Bcl2, BCL2 Apoptosis Regulator; PI-A, propidiumiodide; Annexin V-FIFC, Fluorescein isothiocyanate; OGD, glycose-oxygen deprivation.