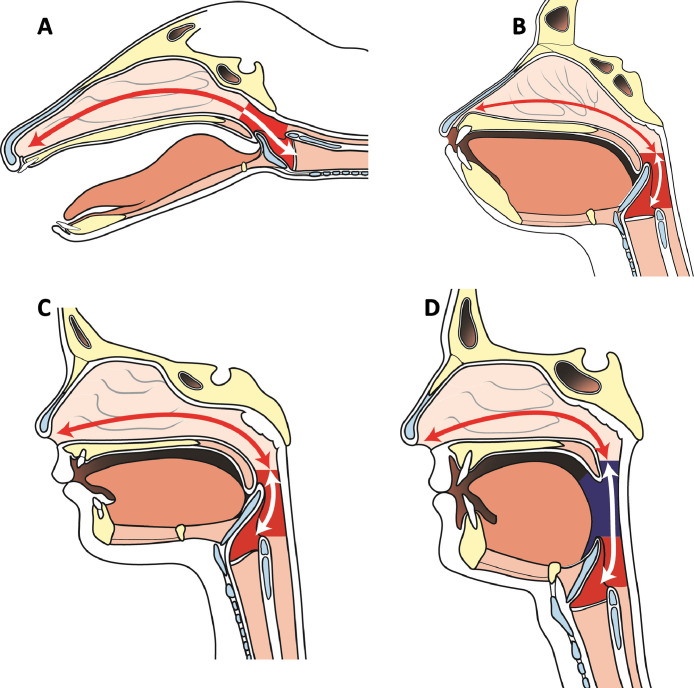
Figure 1.
Supralaryngeal tract angulation in the barking deer (A), ape (B), human infant (C), and adult human (D). The adult human's supralaryngeal tract assumes a tortuous path due to species-specific descent of the larynx which divides the supralaryngeal tract into two roughly equal parts and in so doing facilitates speech. Images areredrawn from pathological specimens printed in the Comparative Anatomy and Physiology of the Larynx.1