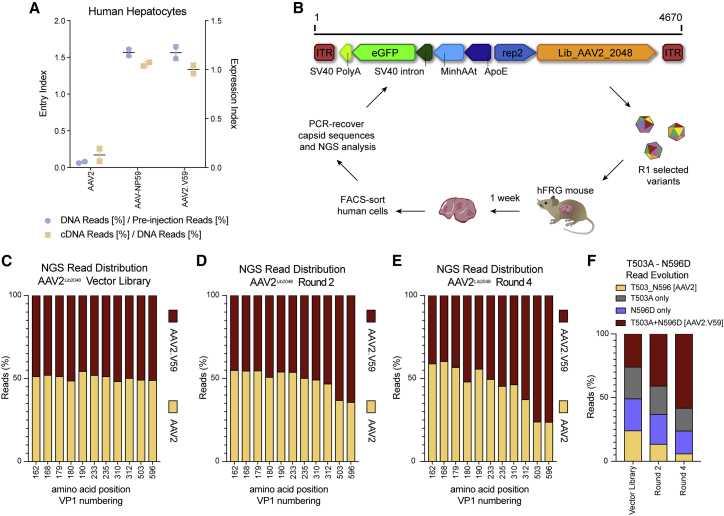
Figure 1.
Validation and in vivo selection of Functional Transduction AAV2Lib2048 library.
(A) In vivo comparison of physical and functional transduction of AAV2, AAV-NP59, and AAV2.V59 capsids in the xenograft liver model. Each AAV variant was used to package two unique barcoded ssAAV-LSP1-GFP-BCWPRE-BGHpA cassettes, and an equimolar mix of all three variants was used. NGS reads mapped to each capsid in human hepatocytes at the DNA level (cell entry, physical transduction, 113.6 vg/diploid human genome) normalized to the pre-injection are shown (entry index). cDNA reads (expression, functional transduction) normalized to the mapped DNA reads are also shown (expression index). (B) Functional transduction (FT) selection platform and the FT selection scheme. The capsid libraries are cloned downstream of the 3′ rep region with the cap expression driven by the p40 promoter. The LSP1-EGFP reporter cassette is positioned in the reverse direction to the p40 cap. (C–E) NGS analyses of amino acid distribution at the 11 positions variable between AAV2.V59 and AAV2, in the packaged library (C), after round 2 (D), and after round 4 (E) of the selection process. (F) NGS read distribution of AAV2 amino acid positions 503 and 596 on the initial packaged library and two subsequent rounds of selection.