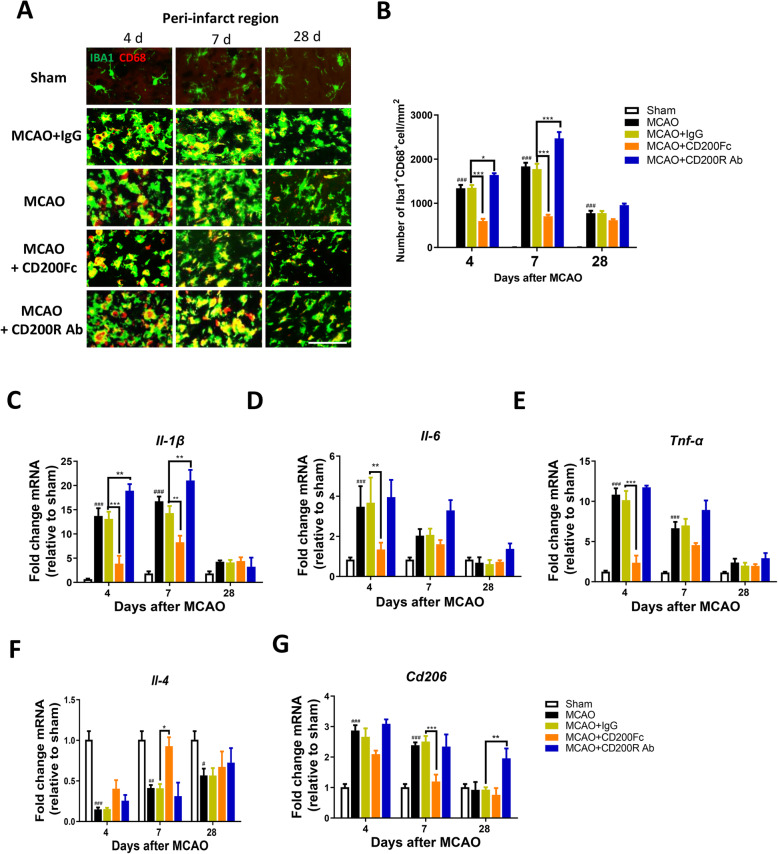
Fig. 6.
Microglia activation and inflammatory release were inhibited via activating the CD200/CD200R pathway after ischemic stroke in rats. Representative sections of brain in different groups were immunostained with iba-1 (green) and CD68 (red, marker of microglia activation) in ipsilateral sensorimotor cortex after MCAO (a) (n = 3, scale bar: 50 μm), CD200Fc decreased the number of iba-1+/CD68+ cells at 4 and 7 days compared with MCAO+IgG group, whereas CD200R Ab reversed the effect. The effect of CD200/CD200R signaling pathway on the mRNA levels of Il-1β, Il-6, Tnf-α, Il-4, and Cd206 in ipsilateral sensorimotor cortex (c–g), (n = 4–5). Results are expressed as means ± SEM. #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01, ###P < 0.001 versus the Sham group. **P < 0.05, **P < 0.01,***P < 0.001 versus the MCAO+IgG group