Fig. 1.
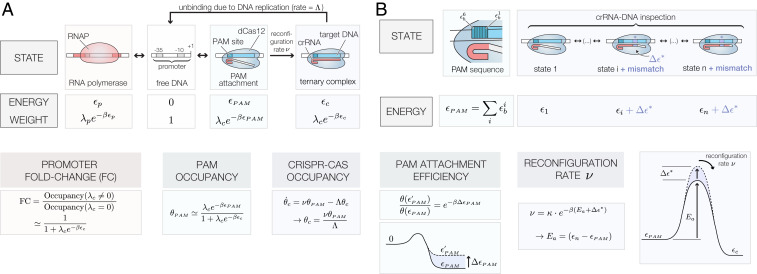
Thermodynamic model of dCas12a binding. (A) Thermodynamic states, energies, and Boltzmann weights of a dCas12a (, where = Boltzmann constant, T = temperature) for the PAM attachment, crRNA–DNA inspection, and reconfiguration steps. The fold change (FC), PAM occupancy , and CRISPR-Cas occupancy depend on the effective PAM energy , the CRISPR-Cas binding energy , and the DNA replication rate . All expressions assume that binding occurs in the weak promoter () and weak PAM binding () limits, where is the fugacity of a dCas12a molecule with chemical potential . (B) Internal base-dependent energies define a PAM-specific binding energy . In this model, the PAM-specific binding energy between two targets with energy that differs by scales their relative PAM attachment efficiency by . The presence of crRNA–target DNA mismatches increases the effective activation energy by a mismatch energy and scales the effective reconfiguration rate by a multiplicative factor equal to .