Figure 1: Synaptic signaling by ZI PV+-neurons is required for fear memory acquisition and recall of remote fear memory.
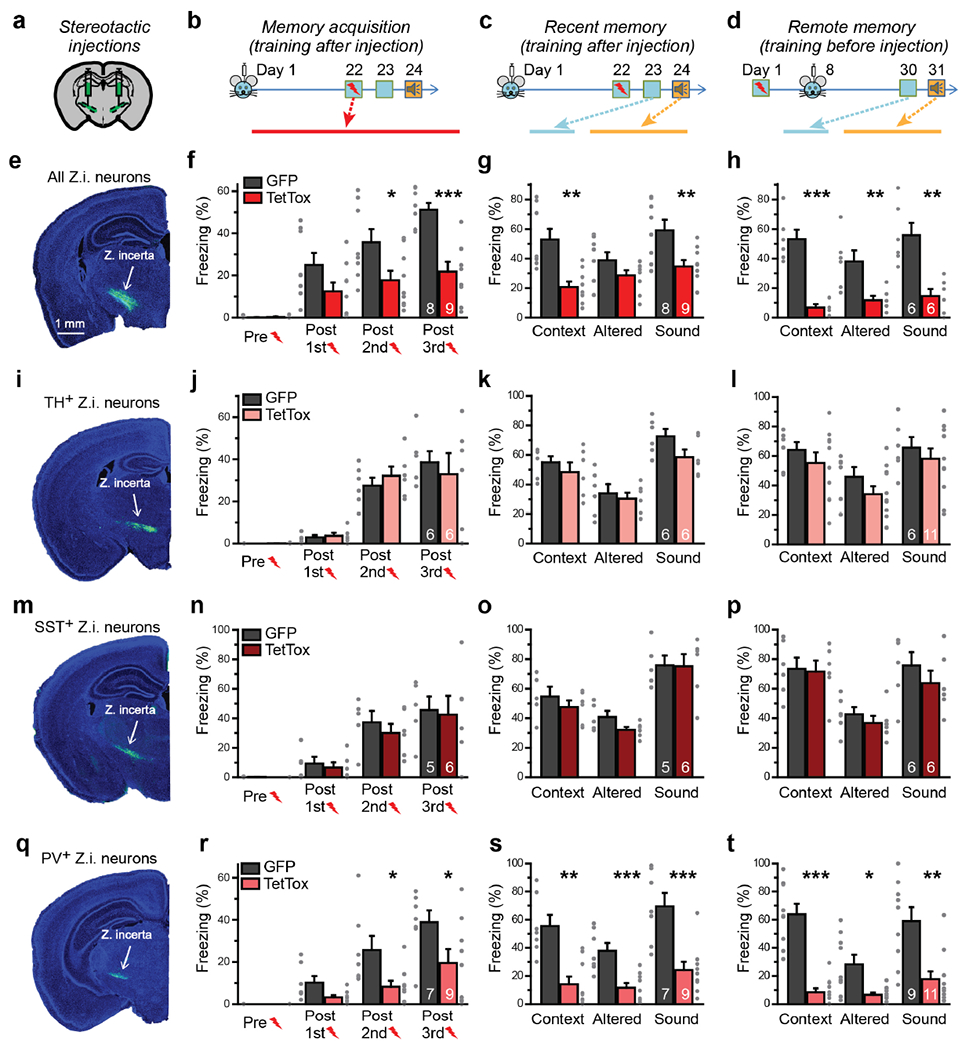
(a-d) Experimental design for fear memory experiments (a, stereotactic injection strategy of AAVs encoding TetTox into the medial ZI; b-d, experimental sequence of injections, fear conditioning training, and freezing behavior observations).
(e-h) Inactivation of all synaptic outputs from the medial ZI (e) impairs fear conditioning training (f; P = 0.8, Mann-Whitney test; P = 0.09, 0.03, 0.00014, two-sided unpaired t-tests), recent fear memory (g; P = 0.00101, 0.13, 0.009, two-sided unpaired t-tests), and remote memory when outputs are inactivated after training (h; P = 4 × 10−4, 0.009, 0.0017, two-sided unpaired t-tests).
(i-l) Inactivation of dopaminergic neurons in the ZI by injection of double-floxed TetTox into TH-Cre mice (i) has no effect on fear conditioning training (j; P = 1, Mann-Whitney test; P = 0.7, 0.4, 0.6, two-sided unpaired t-tests), recent memory (k; P = 0.4, 0.6, 0.08, two-sided unpaired t-tests), or remote memory (l; P = 0.4, 0.2, 0.5, two-sided unpaired t-tests).
(m-p) Inactivation of SST+-neurons in the ZI by injection of double-floxed TetTox into SST-Cre mice (m) has no effect on fear conditioning training (n; P = 0.9, Mann-Whitney test; P = 0.6, 0.5, 0.8, two-sided unpaired t-tests), recent memory (o; P = 0.4, 0.08, 0.9, two-sided unpaired t-tests), or remote memory (p; P = 0.9, 0.4, 0.4, two-sided unpaired t-tests).
(q-t) Inactivation of PV+-neurons in the ZI by injection of double-floxed TetTox into PV-Cre mice (q) impairs fear conditioning training (r; P = 1, Mann-Whitney test; P = 0.07, 0.02, 0.049, two-sided unpaired t-tests), recent fear memory (s; P = 0.002, Mann-Whitney test; P = 8 × 10−4, 9 × 10−4, two-sided unpaired t-tests), and remote memory when outputs are inactivated after training (t; P = 3 × 10−5, 0.014, two-sided unpaired t-tests; P = 0.003, Mann-Whitney test) similar to the inactivation of all ZI outputs.
Quantitative data are means ± SEM. P < 0.05 was considered significant (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001). All numbers of mice used are presented in right bars. For TetTox or EGFP group in all memory acquisition results (f, j, n, r), P < 0.05, F > 7, one-way repeated measures ANOVA.
