Fig. 4.
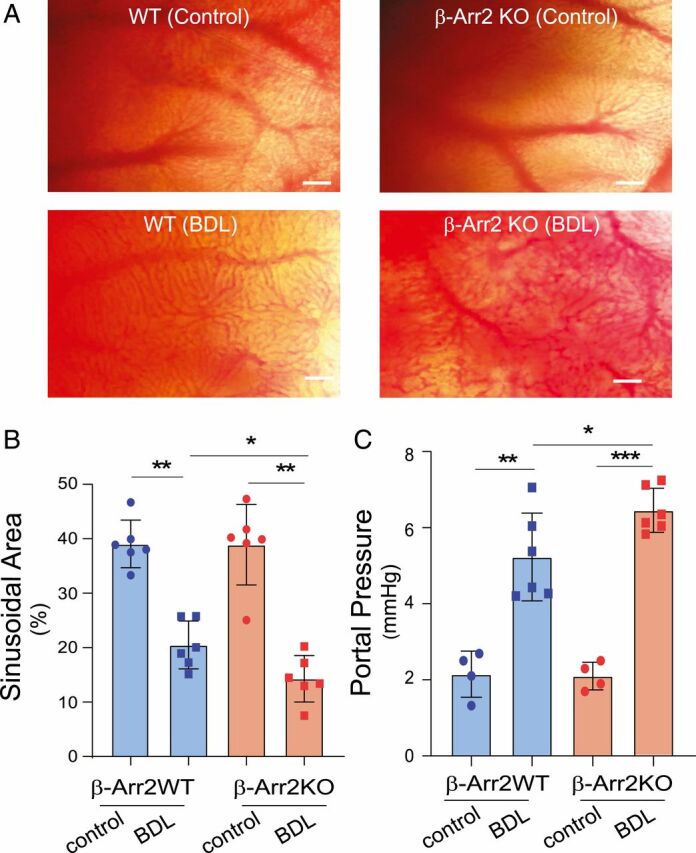
Physiologic effects of β-Arr2 deficiency. (A) Normal or injured (imaging was performed 14 d after BDL) β-Arr2 WT or β-Arr2 KO mice were anesthetized and liver lobes were examined using in vivo microscopy; images of hepatic sinusoids were obtained as described in Materials and Methods. (Scale bars, 50 μm [images are representative of more than 10 fields in each liver, from three different mice]). (B) Sinusoidal volume as in A was quantitated as described in Materials and Methods (n = 6/group). (C) Portal pressure in normal or injured β-Arr2 WT or β-Arr2 KO mice as in A was measured as described in Materials and Methods. Sham surgery was performed as a control (n = 6/group). Statistical significance for B and C was evaluated by one-way ANOVA. Data are mean ± SD, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.005 for differences between indicated groups.
