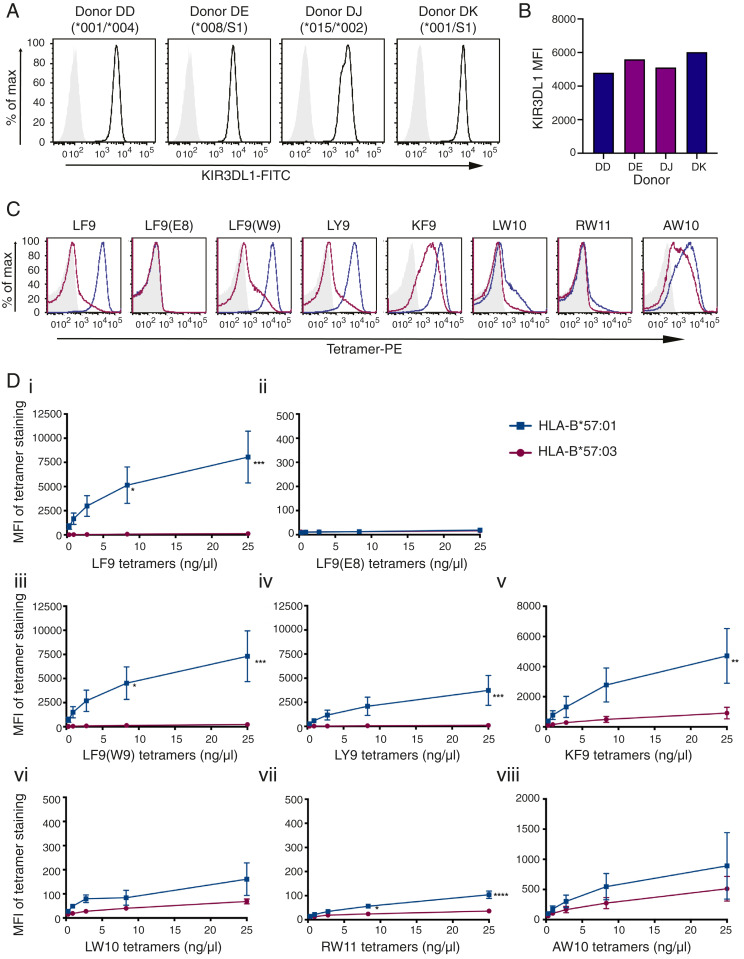
Fig. 3.
Identical peptides loaded onto HLA-B*57:01 and HLA-B*57:03 molecules demonstrate disparate binding to KIR3DL1+ NK cells. (A) NK cells were sorted and expanded from four KIR3DL1+ donors and stained with NKB1-FITC (anti-KIR3DL1). Donors were KIR3DL1 subtyped as High1(*001)/Null(*004), High2(*008)/S1, High2(*015/*002), and High1(*001)/S1. (B) MFI of NKB1-FITC staining on KIR3DL1+ NK cells from each donor is compared (blue, KIR3DL1*001; purple, KIR3DL1*015-like). (C) HLA-B*57:01 and HLA-B*57:03 tetramers loaded with eight different peptides were used to stain KIR3DL1+ NK cells (representative plots for donor DK with 25 ng/μL tetramer: unstained/SA-PE only, light gray; HLA-B*57:01-PE tetramers, blue; HLA-B*57:03 tetramers, magenta). (D) KIR3DL1+ NK cells were stained with HLA-B*57:01 and HLA-B*57:03 PE-tetramers loaded with peptides as follows: (i) LF9; (ii) LF9(E8); (iii) LF9(W9); (iv) LY9; (v) KF9; (vi) LW10; (vii) RW11; or (viii) AW10. Threefold serial dilutions were performed, and the MFI of tetramer binding was plotted. HLA-B*57:01 and HLA-B*57:03 tetramer binding on KIR3DL1+ NK cells across two independent experiments (with two donors each) was compared using a two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparison test [LF9: ***P = 0.0001, *P = 0.0152; LF9(W9): ***P = 0.0003, *P = 0.0344; LY9: ***P = 0.0010; KF9: **P = 0.046; RW11: ****P < 0.0001, *P = 0.0188]. The SEM is depicted.