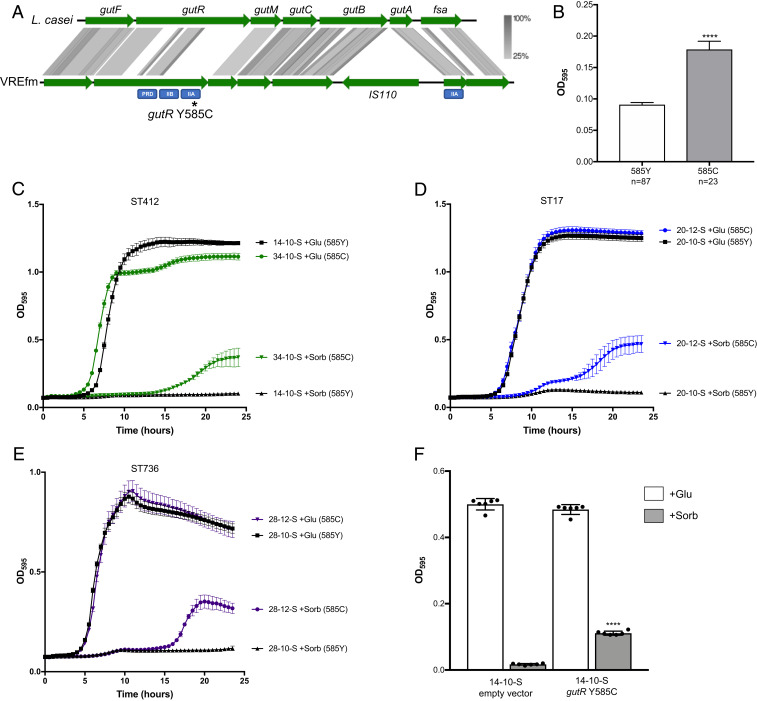
Fig. 3.
A Y585C mutation in the sorbitol operon regulator gutR is associated with VREfm growth in the presence of sorbitol. (A) Alignment of the gut sorbitol utilization operon in L. casei (Top) and VREfm (Bottom). Green arrows indicate coding sequences, and gray shading shows protein sequence homology ranging from 25 to 100%. Predicted functional domains in gutR and gutA are labeled below each gene in blue rectangles. The approximate position of the Y585C mutation in gutR is marked with an asterisk. (B) Association between the gutR Y585C mutation and growth in sorbitol among all 110 VREfm isolates in the dataset. Average bacterial growth ± SD as measured by OD595 after 24 h in a complete defined medium supplemented with sorbitol is shown. ****P < 0.0001 by two-tailed t test. (C–E) Kinetic growth curves of matched gutR wild-type and Y585C mutant isolate pairs in complete defined medium supplemented with glucose (+Glu) or sorbitol (+Sorb). Mean OD595 values ± SDs are plotted for at least three replicates of each isolate grown at 37 °C. The STs of each isolate pair are listed above the plots, and gutR alleles are listed to the right of the growth curves. (F) Expression of the gutR Y585C allele in a wild-type isolate confers growth in sorbitol. Average bacterial growth after 24 h at 37 °C is plotted ± SD for each isolate grown in a complete defined medium supplemented with glucose (+Glu, white bars) or sorbitol (+Sorb, black bars). ****P < 0.0001 by two-tailed t test comparing sorbitol growth versus empty vector.