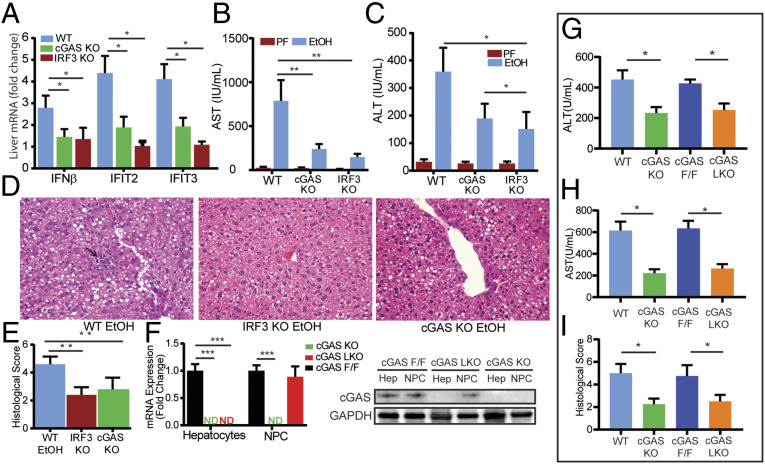
Fig. 2.
Hepatocyte-specific cGAS drives alcohol-induced IRF3 activation and liver injury. WT, cGAS-deficient (cGAS KO), and IRF3-deficient (IRF3 KO) mice were exposed to the 10-d NIAAA chronic and binge alcohol model. (A) Hepatic mRNA expression of IRF3-regulated genes (Ifnβ, Ifit2, Ifit3), (B and C) serum transaminase levels, and (D and E) liver histology and histological scoring (hematoxylin and eosin [H&E], 40× magnification; arrow highlighting an inflammatory foci) from WT, cGAS KO, and IRF3 KO mice. (F) mRNA expression and immunoblot for cGas in hepatocytes and nonparenchymal cells (NPCs) from cGAS F/F, cGAS KO, and cGAS LKO mice. (G and H) Serum transaminase levels and (I) histological score from WT, cGAS KO, cGAS F/F, and cGAS LKO mice exposed to the NIAAA chronic and binge alcohol model. N = 6–10 mice/group. Data are shown as mean ± SD. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.