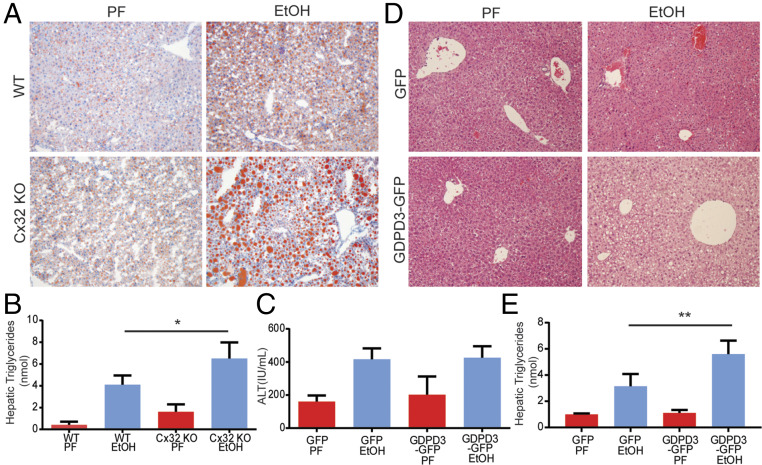
Fig. 5.
Cx32 deficiency induces hepatic triglyceride accumulation and up-regulation of GDPD3. (A and B) WT and Cx32-deficient (Cx32KO) mice were exposed to the chronic and binge ethanol model. (A) Histological evidence of increased lipid deposition in Cx32KO mice compared to WT mice based on Oil Red O staining. (B) Increased hepatic triglyceride content in Cx32KO mice compared to WT mice. (C–E) WT mice were exposed to a modified version of the chronic and binge ethanol model, in which mice were injected on day 9 with either recombinant adenoviral vectors expressing GDPD3-GFP or GFP alone. Mice were then gavaged with 5 g ethanol/kg body weight on day 12 and killed 9 h later. (C) No difference in serum ALT in GDPD3-GFP–infected mice compared to control GFP-infected mice. (D) Increased steatosis based on histological analysis of H&E specimens. (E) Levels of hepatic triglycerides in GDPD3-GFP–infected mice compared to control GFP-infected mice. (Data are shown as mean ± SD and analyzed by Student’s t tests. N = 8–12 mice/group. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.