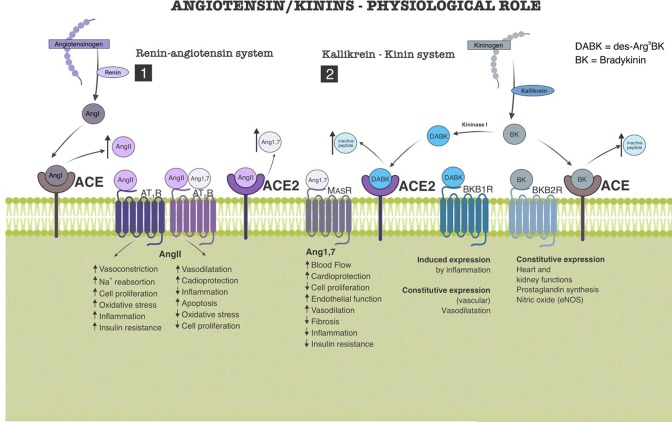
Fig. 1.
Role of renin/angiotensin system (RAS) and kallikrein/kinin system (KKS) in body homeostasis. 1) Renin cleaves angiotensinogen producing angiotensin I (AngI), which is quickly converted to angiotensin II (AngII) by the angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE). AngII binds to two membrane receptors (AT1 and AT2) with antagonistic effects on homeostasis. AT1 activation promotes proinflammatory and increase of blood pressure and AT2 activation produces cardioprotective and anti-inflammatory effects. AT2 is also the target of Angiotensin1-7 (Ang1-7), product of ACE2 enzymatic activity upon AngII, which in turn decreases the concentration of AngII. MasR, another Ang1-7 binding site, produces anti-inflammatory, cardioprotective and hypotensive effects. (2) The crosstalk between the two pathways takes place through the ACEs which have also catabolic activities on bradykinin (BK) and its analog, des-Arg9BK (DABK). BK and DABK are products of KKS. Through kallikrein, kininogen is cleaved generating BK which is, metabolized to DABK by kininase I. The BKB1R receptor (activated by DABK), in physiological conditions, has basal activity (constitutive) and promotes vasodilation, but is upregulated in inflammatory conditions, with important effects in this scenario. BKB2R (activated by BK) is constitutive and participates in the homeostasis of organs such as heart and kidney.