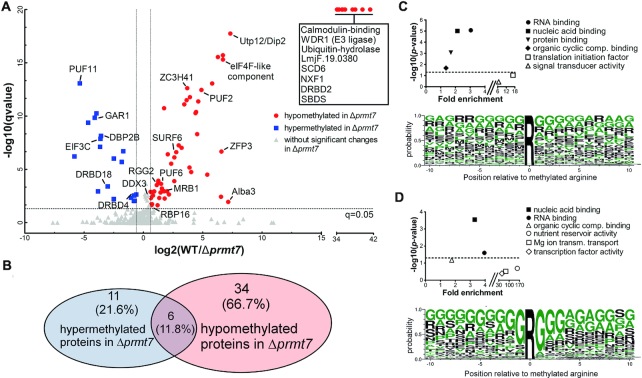
Figure 2.
RNA-binding proteins are putative substrates for PRMT7 arginine monomethylation. (A) Methyl-SILAC peptide pairs were analyzed according to their methylation status in WT versus Δprmt7 Leishmania major cells. Mass spectra quantification of each light and heavy pair ratios detected peptides with increased (hypermethylated, in blue) or decreased (hypomethylated, in red) methylation in Δprmt7 as compared to WT. Methylated RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) are shown as well as proteins that had no methyl peptides detected in Δprmt7 (boxed RBPs). Of 247 identified proteins with isolated MMA peptides, 62 are RBPs; 17 of which are hypomethylated in Δprmt7 (Hochberg and Benjamini test q< 0.05). (B) 51 proteins are differentially methylated between WT and Δprmt7; 6 of which are both hypomethylated and hypermethylated at different residues. (C, D) Significantly enriched Molecular Function Gene Ontology (GO) Terms (upper panel) and selected amino acid residues (lower panel) in the whole MMA proteome (C) versus Δprmt7 hypomethylated proteins (D). For the global data, RNA binding was highlighted (upper panel), yet there is no clear consensus MMA site sequence (lower panel). RNA binding remains characteristic of Δprmt7 hypomethylated proteins, and an enrichment for the ‘RGG’ motif is evident (lower panel). Dotted lines in upper panels depict Bonferroni P-value = 0.05.