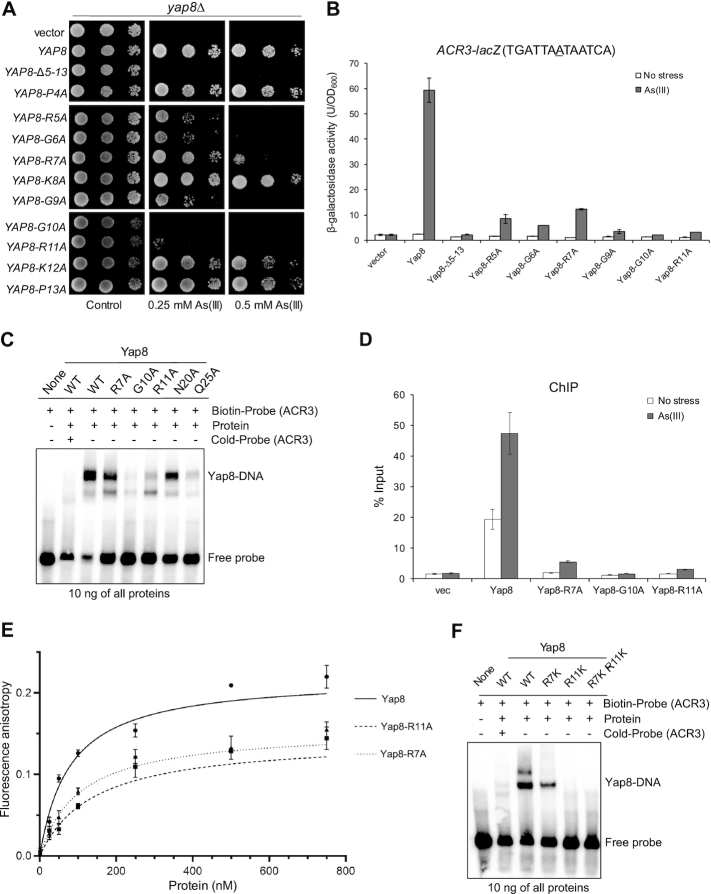
Figure 5.
Functional analysis of Yap8 N-terminal tail mutants. (A) Complementation of As(III) sensitivity of yap8Δ by indicated Yap8 variants. The yap8Δ mutant was transformed with empty vector (pYX122) or plasmids expressing Yap8 variants. The resulting transformants were spotted on minimal selective plates containing various concentrations of As(III) and incubated 3 days at 28°C. (B) β-galactosidase activity driven by the ACR3-lacZ promoter was measured in the yap1Δ yap8Δ mutant expressing indicated Yap8 mutant proteins. Cells were exposed to 0.1 mM As(III) for 6 h or left untreated for the control. The values are the means of three biological replicas performed in triplicate ± S.D. (C) Binding of Yap8 variants to the ACR3 promoter as determined by EMSA. Purified GST-Yap8 variants at indicated concentration were incubated with biotin-labeled oligonucleotides corresponding to Y8RE-containing promoter fragments of ACR3 gene followed by electrophoresis. (D) Binding of Yap8 variants to the ACR3 promoter as determined by ChIP. yap8Δ cells bearing plasmids expressing Yap8-HA variant proteins or the control vector were exposed to 0.5 mM As(III) for 30 min or left untreated. qRT-PCR was performed with chromatin fragments immunoprecipitated with anti-HA antibodies and primers amplifying the ACR3 promoter region containing Y8RE1 and Y8RE2 motifs. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean from at least two independent biological replicas and four PCR reactions. (E) Fluorescence anisotropy assays performed with indicated variants of purified GST-Yap8 and the FAM-labeled ACR3 promoter fragment as described in Materials and Methods. (F) R7K and R11K variants of Yap8 are defective in binding to the ACR3 promoter as determined by EMSA.