Figure 3.
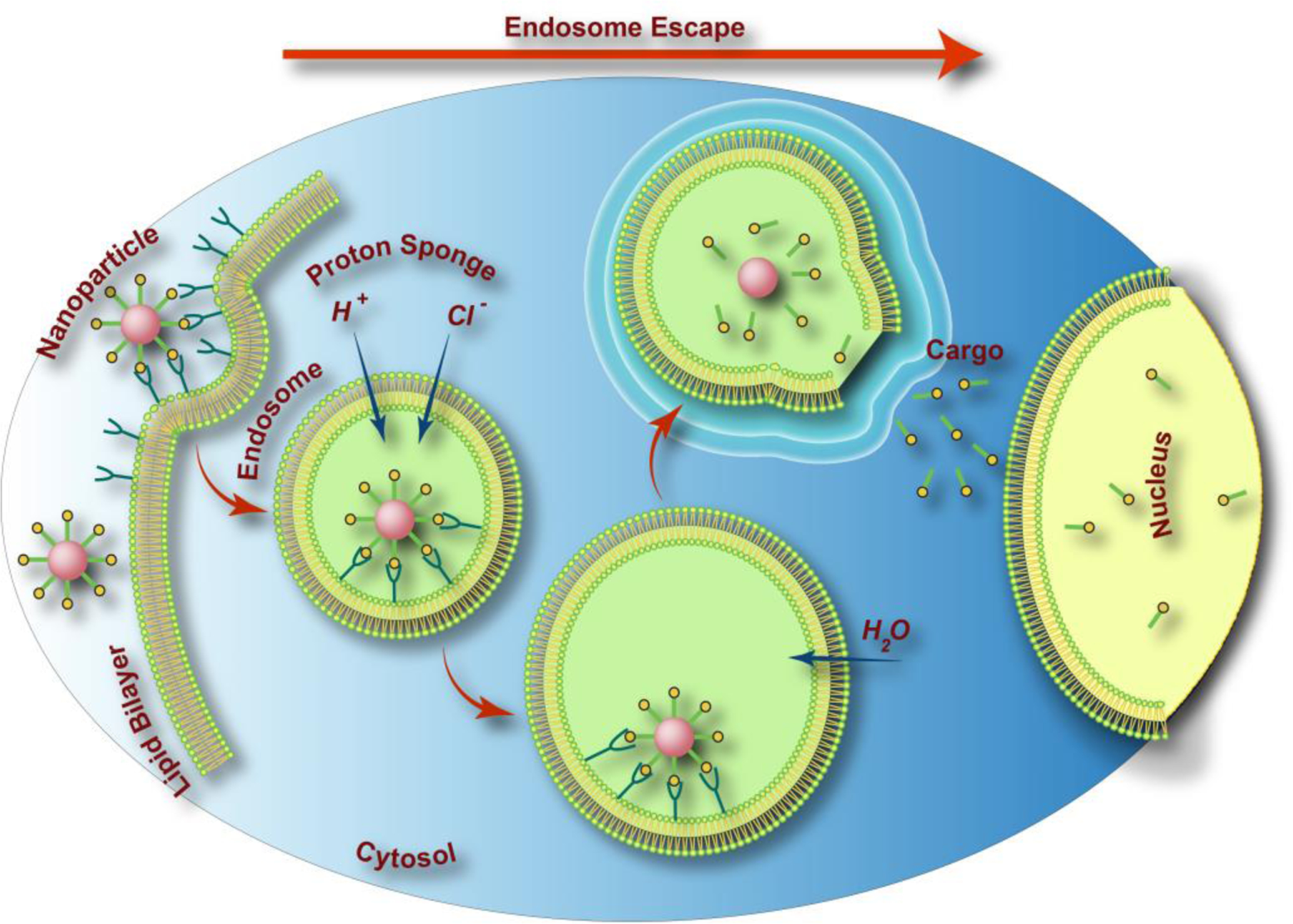
Schematic drawing of CaP’s endosomal escape in cancer cells through the proton-sponge effect. The maturation of endosome to lysosome creates the acidic environment that along with various enzymes degrades the content of lysosome (e.g., CaP nanoparticles). H+ ions diffuse into the endosomes by proton pumps and subsequently for maintaining the charge neutrality Cl− ions enter to this vesicle. The influx of these ions along with influx of water causes the endosomes to swell and rupture, releasing its trapped payload inside the cytosol, a process generally known as endosomal escape.
